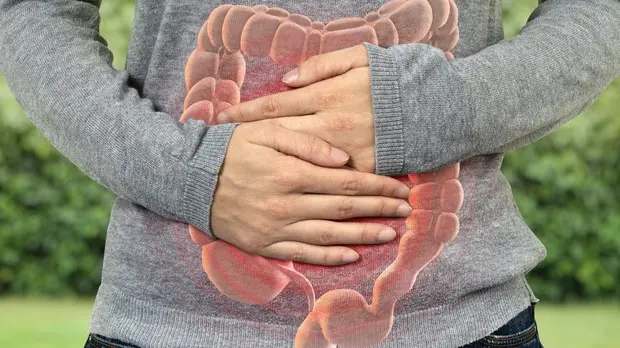
Located in the abdomen area, the colon forms, together with the rectum, the large intestine, i.e. that part of the digestive system mainly responsible for absorbing water from what remains of food passed through the stomach and small intestine, to then compact the feces before their expulsion. A fundamental function for the well-being of the entire organism, which subjects the organ to considerable “stress”: just think that every day between 800 and 1,800 ml of liquids flow into the colon from the small intestine: of these, only between 40 and 400 ml are then passed through the faeces.
Anatomically, the colon looks like a hollow organ (or viscera) that starts from the ileocecal valve, the terminal section of the small intestine, and ends with the rectum and the anal canal. It is about one and a half meters long and is divided into different parts: cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon.
Mucosa, submucosa, muscular and serosa are instead the four layers that make up the wall of the organ, going from the inside to the outside. In particular, the first is formed by two different types of cells linked to the two main functions performed by the colon: the epithelial ones, useful for the absorption of water and salts; the muciparous goblet-shaped ones, which produce a mucous and slimy substance capable of facilitating the transit of faeces.
Cancer risk
When epithelial cells grow uncontrollably, colon cancer is generated, one of the most widespread neoplasms currently and by far the main one in the intestine. According to estimates provided by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), colorectal cancer represents 10% of all cancers diagnosed worldwide and ranks third behind female breast cancer and lung cancer. In Italy in 2022, around 48,100 new diagnoses were estimated, distributed similarly between men and women: more than just those of breast cancer. According to what the AIRC (Italian Association for Cancer Research) affirms, the incidence in our country in the last twenty years has decreased for both sexes, and even more evident has been the reduction in mortality from colon cancer. rectum, with rates decreasing by about 10 per cent in the last five years. All these advances are mainly linked to the expansion of screening programs and early diagnosis, but also to improvements in medical and surgical therapies. According to the latest report “The numbers of cancer in Italy” by Aiom (Italian Association of Medical Oncology) in our country there are 513,500 people living after a diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Other pathologies
Most colon cancers arise from the malignant transformation of polyps, small growths generated by the proliferation of intestinal mucosa cells. Not all polyps evolve into malignant neoplasms: the risk increases with the increase in size, the simultaneous presence of multiple polyps or if areas of dysplasia are found.
The most common form of colon cancer is adenocarcinoma; decidedly rarer are squamous cell carcinoma and undifferentiated carcinoma.
However, cancer is not the only pathology that can affect this particularly delicate organ. It is in fact among the areas where Crohn’s disease occurs most frequently, a chronic inflammatory disease that manifests itself with diarrhea and abdominal pain: an affection that can lead to complications such as stenosis, i.e. a narrowing of some sections of the intestine . Another pitfall is represented by ulcerative colitis, which originates in the anus and then extends to the colon. It involves the presence of diarrhea and mucus in the stool, sometimes even stained with blood, and is often characterized by ulcers.
Also pay attention to irritable bowel syndrome, which involves abdominal pain and altered intestinal activity, often in subjects subjected to strong periods of stress. Finally, diverticulosis, characterized by small “pockets” that form in the colon: if left untreated, it can evolve into diverticulitis, up to bowel perforation.
***
Correct lifestyles and regular checkups
Despite being among the most common malignancies, colorectal cancer is not easy to identify. The reason? Symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, blood in the stool, meteorism and abdominal swelling are often common to those of other pathologies (such as hemorrhoids or various inflammations). Moreover, in the initial stage the tumor does not cause any disturbances. This is why it is essential to undergo periodic check-ups and consult a specialist when any intestinal problems do not improve within a few weeks. In addition to the alarm bells already listed, other signs such as weight loss without apparent cause, tiredness and anal itching should not be overlooked.
Risk factors and prevention
There are several risk factors associated with colon cancer. The first is age, since the disease mainly occurs after the age of 60. The genetic factor also affects: the probability of cancer increases if there have been cases of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or Lynch syndrome in the family. The risk also increases in the presence of chronic inflammation, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Other factors, on the other hand, are linked to incorrect lifestyles: a diet rich in animal fats, red meat, sausages and low in fibre; obesity and sedentary lifestyle; smoke; alcohol abuse.
Already from this quick overview it clearly emerges how healthy daily habits are the basis of the prevention not only of colon cancer, but also of all the other pathologies connected to this area of the intestine. So make way for fruit, vegetables and fibers on the table, limiting red meats, cured meats and alcoholic beverages. It is also important to practice physical activity every day, even in a moderate form, and to constantly keep your body weight under control. Finally, an absolute stop to cigarettes and tobacco.
Fundamental exams
According to estimates, colorectal cancer caused around 21,700 deaths in Italy in 2021. A still high number, which however has decreased in recent years: the assessment in the initial stages of development, before the pathology causes disturbances, makes this type of cancer increasingly curable today. For this to happen, the role of controls is fundamental.
Screening to discover colorectal cancer is part of the prevention program organized and proposed by the National Health Service, every two years, to all people between 50 and 69 years of age. The basic diagnostic test is the search for occult blood in the stool, which is followed by further tests such as, for example, a colonoscopy, an examination that allows the doctor to explore the internal walls of the large intestine and rectum. Only a small part of the screening programs active in Italy foresees, instead of the search for occult blood, rectosigmoidoscopy performed only once at the age of 58-60 years.
The ISS data show that unfortunately the national coverage of colorectal screening is still rather low: in the two-year period 2020/21 it was 44% for the 50-69 age range, with a strong variation between the Northern regions (all over 67%) and those of the South, on average around 25%. Sardinia, with 42.4%, is in line with the national average.
***
Irritable bowel: persistent and difficult to overcome disorders
Stomach ache, bloating, diarrhea and constipation: these are symptoms that practically everyone has had to live with at some point. But when the problems are persistent and significantly impact the quality of life, we speak of irritable bowel syndrome (or spastic colitis). This condition affects about 10% of the population, so much so that it is the second cause of absence from work, beaten only by the seasonal flu. Symptoms are usually not continuous, but occur intermittently over a long period of time.
Few certainties
The causes of the onset have not been well clarified: the main hypotheses are related to the passage of food through the intestine too fast or too slow, to stress, to alterations of the intestinal bacterial flora and also to the presence of other cases in the family. And, just as there are no certainties about the causes, there is also a lack of certainty about the possible remedies for irritable bowel syndrome. However, the important thing is to consult with your doctor in order to evaluate whether intestinal disturbances are “indicators” of more serious pathologies such as colon cancer. Blood tests are also useful, to rule out celiac disease and the possible presence of inflammatory bowel conditions, and stool tests. Since there are no specific therapies, one can try to mitigate the disorders related to irritable bowel syndrome through diet and lifestyle. Those dealing with diarrhea should try to cut down on high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, nuts, hazelnuts, and seeds, and avoid products containing sorbitol. Conversely, in case of constipation it is advisable to drink plenty of water, take more fiber and increase physical activity. In case of bloating, cramps and flatulence, carbonated drinks and some types of vegetables (cauliflower, peas, broccoli, beans) should be limited and chewing gum should not be chewed.
© breaking latest news