This article is reproduced from CASE Science News “How big is the sky?” Distance in Astronomy (1)—From Earth to Sun”
How to measure length or distance in astronomy? The rulers, tape measures, and laser rangefinders commonly used on earth may not be so suitable. There are still methods for direct measurement of relatively close celestial bodies, and some indirect inferences can only be relied on for long-distance objects. We start from the ancient Egypt using wells, minarets, and camels to calculate the circumference of the earth, and then introduce methods to measure the distances of the moon and planets in the solar system using radar astronomy and other methods.
The circumference of the earth: wells, minarets, camels
How do we usually measure the length or distance? If it’s a small thing on the table, we can use a ruler; if it’s a little farther away, we can use a tape measure; if it’s a little farther away, we can use a laser rangefinder. These are common and commonly used distance measurement tools on the earth. What to do when the distance is farther? How should we measure the circumference of the earth? How far is the moon and the sun? What about more distant celestial bodies?
We cannot reach the sky in one step. It is necessary to measure directly from the closer one, and then find a way to indirectly calculate the distance of distant celestial bodies. Let’s start with the nearest “Earth Circumference” first! In fact, as early as in ancient Greece, Pythagoras had already proposed the idea that the earth is a “ball.” The Egyptian scholar Eratosthenes estimated a value for the circumference of the earth in 240 BC. This algorithm is very interesting, let’s take a look at Figure 1 together.
First of all, he knew that on the day of the summer solstice, he could see the reflection of the sun from directly above from a well in the Egyptian city of “Syene (now Aswan).” In other words, on the summer solstice day, the sun will just hit Saiini directly. He further measured the length of the shadow of the obelisk in Alexandria on the day of the summer solstice. From the length of the shadow and the height of the obelisk, the zenith angle α of the sun can be calculated.And because of the similarity of triangles, this zenith angle a At the same time, it will be the angle between Saiini and Alexandria on the earth.This zenith angle a It is about 7.2°, because 7.2° occupies 1/50 of the 360° of the entire circle, so multiply the distance by 50 to get the circumference of the earth.
In other words, as long as you find the distance between Sainy and Alexandria, and multiply it by 50, it is the circumference of the earth… But how do you know the distance between the two cities? He asked from the caravan that the two cities had to let the camels walk for 50 days. After some calculations and conversions, he found that the circumference of the earth was about 252,000 “stadia” (the unit of distance in Egypt at the time). Although the conversion between the unit “stadia” he used and the modern length unit cannot be verified, modern scientists believe that the number he measured is between 39,690 kilometers and 46,620 kilometers, which is only 1%-15 from the modern accepted value. % Only![3]
Moon distance: lunar eclipse, laser, mirror
Once we have the size of the earth, let us measure the moon again! Start by measuring the distance between the Moon and the Earth. One of the methods is to use a “lunar eclipse.” This method can be traced back to the Greek astronomer Aristarkhos (310-230 BC). In fact, he was the first to put forward the heliocentric theory in the breaking latest news, but unfortunately he has not been widely recognized. A lunar eclipse is the shadow of the moon entering the earth. Dividing the size of the earth’s shadow by the time of the lunar eclipse is the speed of the moon’s movement. By multiplying the speed of the moon by the time it takes for the moon to make a circle (about 28 days), you can get the circumference and radius of the moon around the earth.
A more modern and more direct method is “laser ranging”. The principle is similar to that of a laser rangefinder. Launching laser light from the earth to the moon, by measuring the reflected light, we can know the time it takes for the light to go back and forth, and multiply it by the speed of light to get the distance to the moon. This time is about 2.5 seconds, and the converted moon-to-earth distance is about 380,000 kilometers.
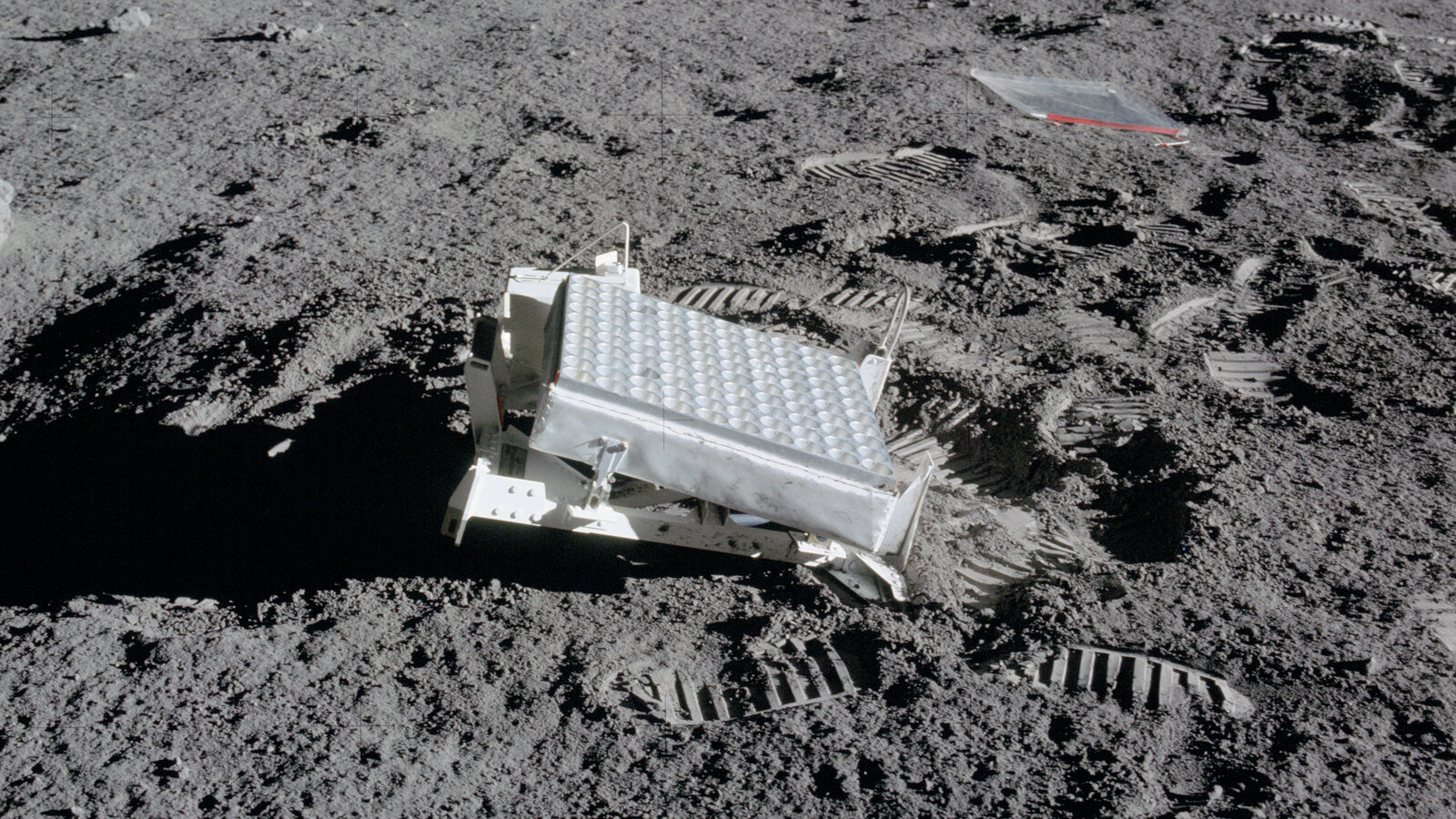
In order to have a better laser light reflection effect, humans also placed 5 reflectors on the moon, which were placed in the 5 missions of human landing on the moon (3 times in the United States and 2 times in the Soviet Union, see Figure 2). These reflectors have improved the precision of the distance between the moon and the earth to the millimeter level. There is a fragment of this experiment in the famous American life comedy series “The Big Bang Theory”, readers may wish to check it out: Learn English with The Big Bang Theory: Blowing up the Moon (subtitled, English teaching version).
Accurate measurement of the distance between the moon and the earth also brings us interesting discoveries.For example, it is discovered or measured that the moon is getting farther and farther away from the earth at a rate of 3.8 centimeters every year; the moon may have a liquid core that is one-fifth the size of the moon’s radius; besides the original motion, the moon has additional shaking. Called “libration”… etc. [5]。
Planetary distance: radar
The method of measuring the distance of a planet is similar to the method of measuring the distance of the moon, except that the distance of the planet is usually too far away. If the general laser light is used, the effect is not good. You must switch to the microwave band. This school is called “radar astronomy (radar astronomy). astronomy)”. The equipment used in radar astronomy must be able to emit high-power microwaves into the universe. In the past, the commonly used observatories included “Arecibo Observatory” and “Goldstone Observatory” (see Figure 3).
(Extended reading: Goodbye: Arecibo Observatory!)
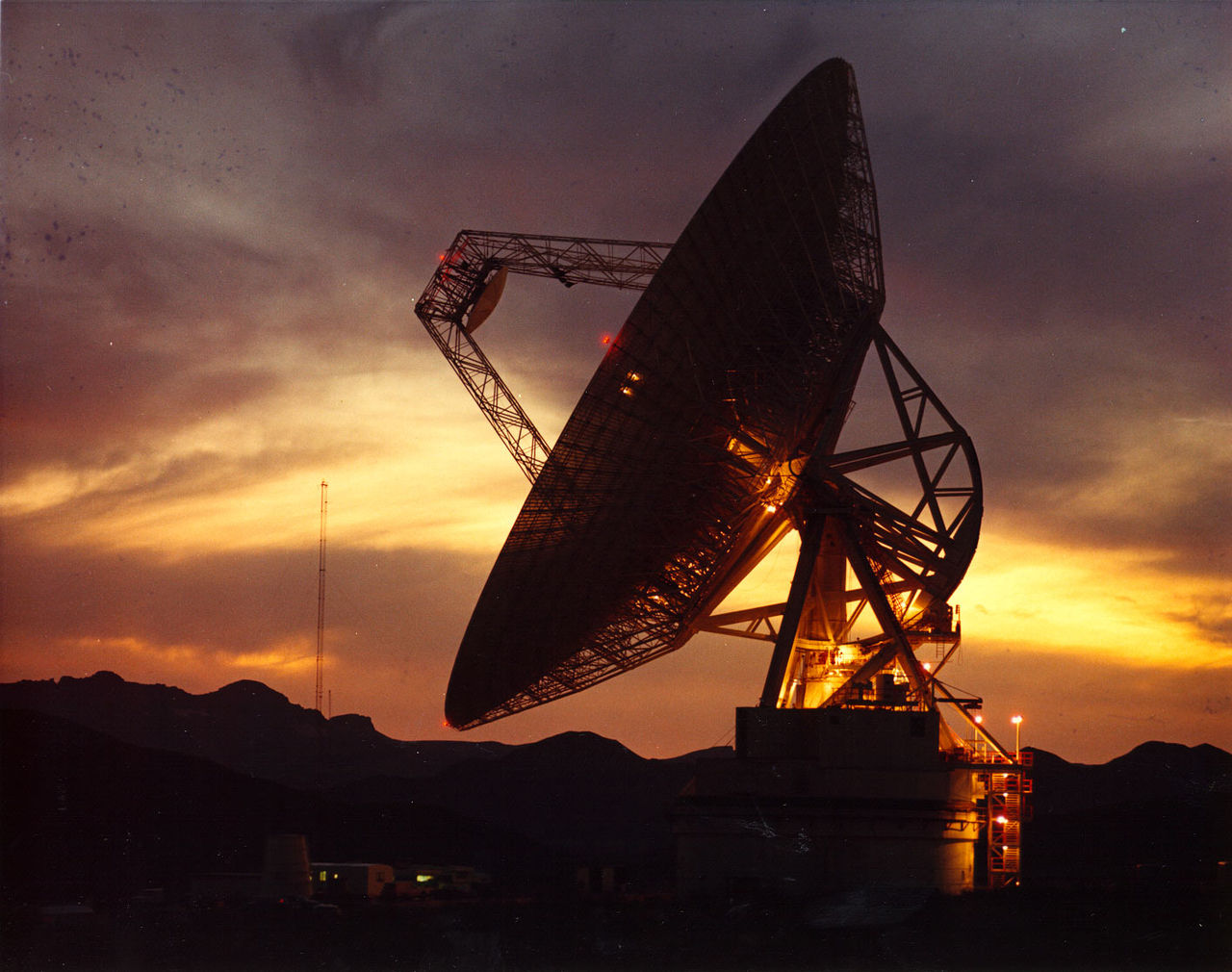

Radar astronomy is used to study the celestial bodies in the solar system. After all, the reflected signal will be too weak if it is farther away.In the past, radar astronomy not only helped us measure the distance of planets, but also used it to observe the surface conditions of celestial bodies. [7]。
Sun’s distance: transit of Venus
The average distance between the earth and the sun is called an “Astronomical Unit (AU or au)”. If you want to measure the distance between the sun and the earth, there is no way to use a laser to measure the distance. The sun’s own light is too strong, and there is no way to reflect laser light or microwaves, and it is impossible for people to install a mirror. What should I do? We can use “Venus Transit” to help!
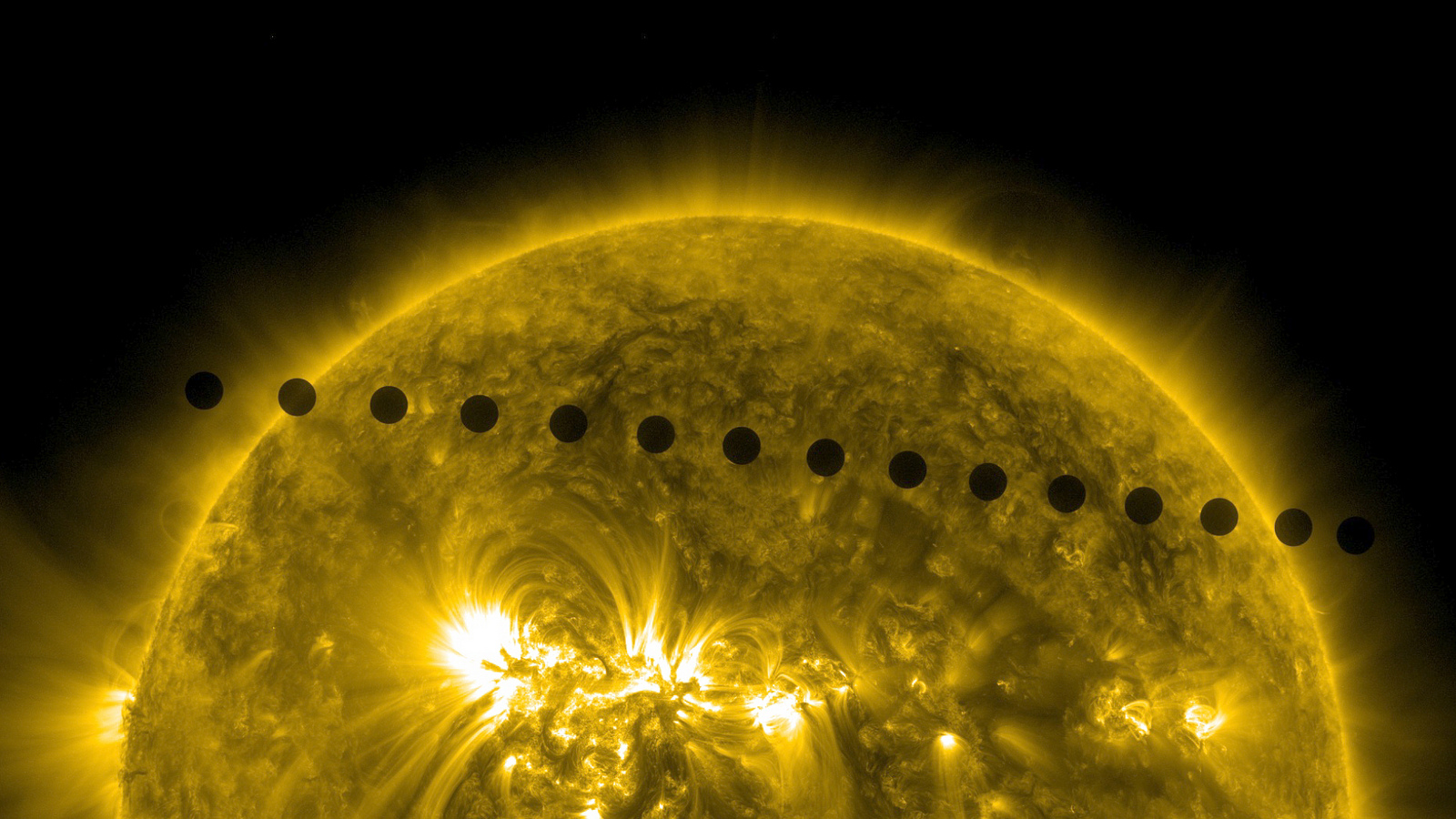

The transit of Venus refers to the phenomenon that Venus passes in front of the sun as seen from the earth (Figure 4). And this is also when the sun, Venus, and the earth are close to a straight line. It’s like when we cover the sun with our hands, the sun, hands, and our eyes will line up in a straight line.
According to Kepler’s law, we can calculate that the orbital radius of Venus is 0.72 astronomical units. The earth’s orbit radius is 1 astronomical unit. When the sun, Venus, and the earth are aligned, the distance between Venus and the earth is 0.28 astronomical units. At this time, as long as you measure the distance of Venus, you can calculate the size of 1 astronomical unit!
However, in this state, the sun behind Venus will seriously interfere with the signal, so it is impossible to use radar to measure the distance of Venus. You have to rely on other methods to find the distance, this method is called “parallax (parallax)”. As for how to use parallax, how to make Danish astronomers and Tycho use the right data, the right instruments, the right inferences, and get completely wrong results, it is another story.
(to be continued)
Reference
- Free Images / Bedouin watching a caravan passing by near the pyramids of Giza
- Eratosthenes | Biography, Discoveries, Sieve, & Facts | Britannica
- wiki / Eratosthenes
- The New York Times / How Do You Solve a Moon Mystery? Fire a Laser at It
- wiki / Lunar Laser Ranging experiment
- wiki / Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex
- wiki / Radar astronomy
- SPACE / Venus Crosses the Sun for Last Time Until 2117, Skywatchers Rejoice
Other articles in this series
How old is the sky?The distance in the universe (1)-from the earth to the sun
How old is the sky?The distance in the universe (2)-from the sun to neighboring stars
How old is the sky? Distance in the universe (3)-“Census”
How old is the sky?Distance in the universe (4)-Cepheid variable star

