[Notice]For customers from the European Economic Area (EEA) and the United Kingdom – Yahoo! JAPAN
From Wednesday, April 6, 2022, Yahoo! JAPAN is no longer available in the EEA and the United
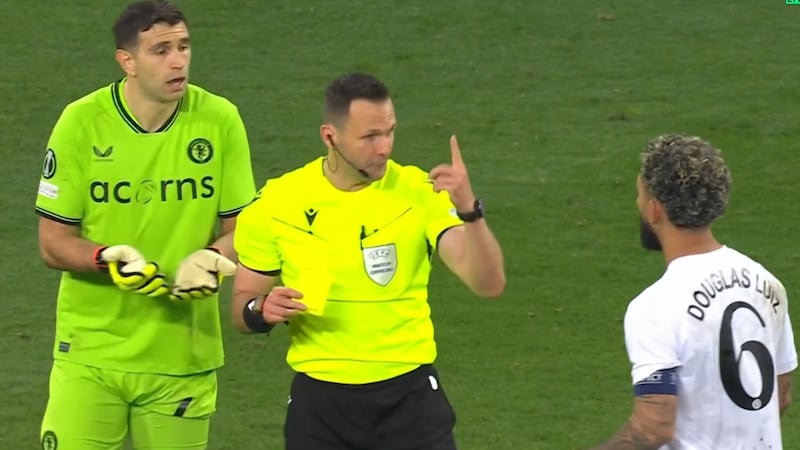
Emiliano Martinez received two yellow cards against Lille, but was allowed to stay on the field and saved penalties
In the penalty shootout, Aston Villa goalkeeper Emiliano Martínez provoked the home fans. That earned him his
Operation Praetorian: MP requests preventive detention for Madureira and “Polaco” | public ministry
This Tuesday, the Public Prosecutor’s Office (MP) requested preventive detention for Fernando Madureira, leader of the Super
Popular Stories

FC Bayern will face Real Madrid in the semi-finals
Bayern Munich has reached the semi-finals of the Champions League for the first time since the 2020
[Notice]For customers from the European Economic Area (EEA) and the United Kingdom – Yahoo! JAPAN
From Wednesday, April 6, 2022, Yahoo! JAPAN is no longer available in the EEA and the United

Emiliano Martinez received two yellow cards against Lille, but was allowed to stay on the field and saved penalties
In the penalty shootout, Aston Villa goalkeeper Emiliano Martínez provoked the home fans. That earned him his
Operation Praetorian: MP requests preventive detention for Madureira and “Polaco” | public ministry
This Tuesday, the Public Prosecutor’s Office (MP) requested preventive detention for Fernando Madureira, leader of the Super
Travel & Explore the world

FC Bayern will face Real Madrid in the semi-finals
Bayern Munich has reached the semi-finals of the Champions League for the first time since the 2020
[Notice]For customers from the European Economic Area (EEA) and the United Kingdom – Yahoo! JAPAN
From Wednesday, April 6, 2022, Yahoo! JAPAN is no longer available in the EEA and the United

Emiliano Martinez received two yellow cards against Lille, but was allowed to stay on the field and saved penalties
In the penalty shootout, Aston Villa goalkeeper Emiliano Martínez provoked the home fans. That earned him his
Operation Praetorian: MP requests preventive detention for Madureira and “Polaco” | public ministry
This Tuesday, the Public Prosecutor’s Office (MP) requested preventive detention for Fernando Madureira, leader of the Super
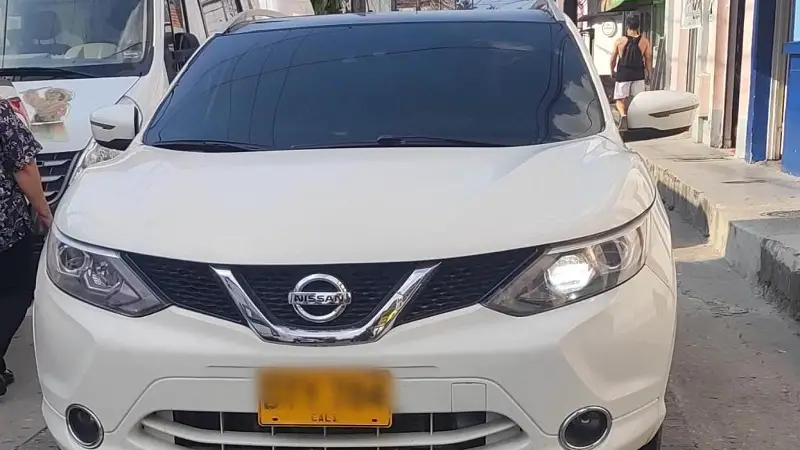

In La Plata, Huila, a high-end truck stolen in Cali was recovered
In an operation carried out in the municipality of La Plata, the Police recovered a high-end truck

Friday’s gossip: Musiala, Isak, Olise, Sesko, Lijnders, Gnabry, Gibbs-White
Bayern Munich forward Jamal Musiala is emerging as Manchester City’s top target for the summer, while Chelsea
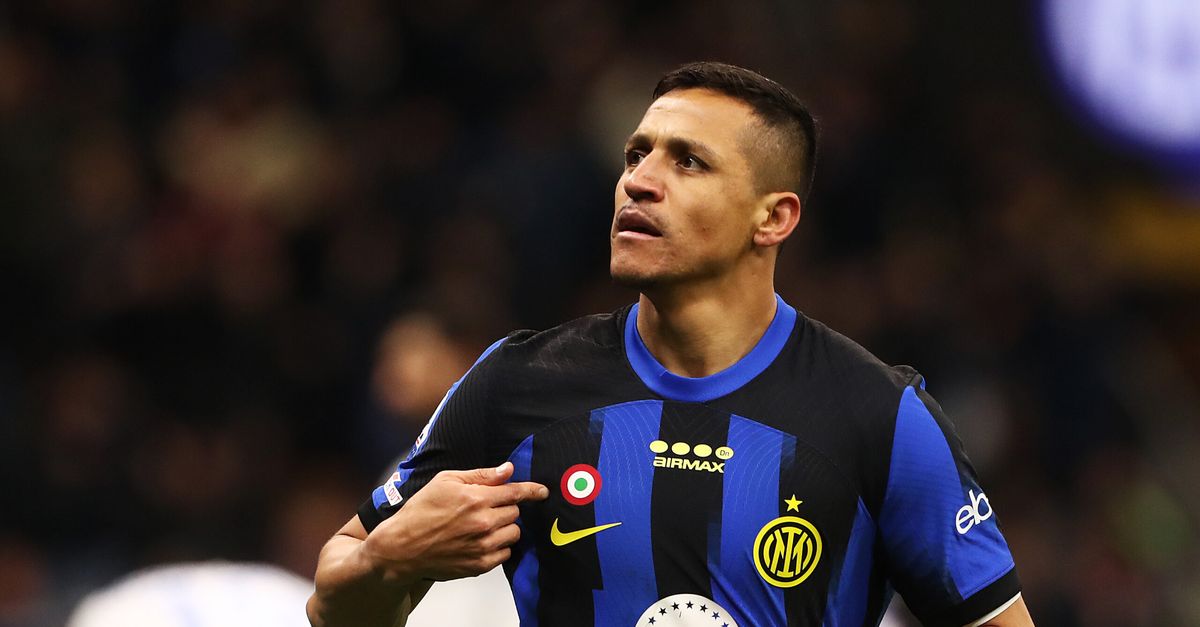

Udinese transfer market – Balzaretti studies the coup: the details of the Sanchez deal
Federico Balzaretti starts working in view of the next championship season. Here are all the details on