[Introduction]Recently, the 2022 Nobel Laureate Philip Dibwig has attracted attention for his resignation as the Dean of the Financial Research Institute of a Chinese University one year before the award. The statement that “Nobel Laureate was eliminated due to substandard assessment” is in circulating online. Although there are many reasons for self-media clarification on the Internet, it is not the assessment, and it is pointed out that the financial research institute is a “non-editing unit” that does not need assessment, but as the commentator said, the reason why this rumor spread widely in a short time is because domestic universities The academic championships of China are becoming more and more intense, and the “promotion or leave” system behind the performance appraisal is even more tormenting for young scholars.
Based on an interview with young liberal arts teachers and administrators of a “double first-class” university, this paper finds thatPerformance evaluation has brought enormous rigid pressure to young teachers, prompting them to adopt the action strategy of “survival first and development later”.Although strategies such as “chasing” hot spots, “doing” hot spots, and actively “irrigating water” do not conform to the value recognition of young teachers, these strategies are generally implemented in practice. The interviewers referred to the establishment as “overcoming the hurdle”. In order to “overcome the hurdle”, they had to temporarily give up their research interest, sacrifice part of the research quality, and then concentrate on research with long-term value after obtaining a stable “iron rice bowl”.
The author states that,Young teachers are the main bearers of students’ teaching, but it is the scientific research results that really decide whether they can be promoted or not.Teaching and educating people is a teacher’s duty, but under the assessment of scientific research, many young teachers have difficulty in effectively balancing scientific research and teaching. The acquiescence of colleges and even schools makes such problems occur widely and repeatedly. In order to meet the academic performance standards, some young teachers have to adopt the strategy of “holding the thighs” of their academic predecessors, trying to publish papers, win projects, and gain social capital.
This study believes that the rigid pressure of the university’s “promotion championship”, the demonstrative power of peers, and the organization’s intentional guiding power, the three forces combine to promote the action logic of “survival first and then development” for young teachers.After the rumors that Nobel Prize winners were dismissed due to assessment, what deserves more attention and consideration is the situation of young university teachers, because their fate and role are related to the future of education and scientific research in China.
This article was originally published in the 7th issue of “Exploration of Higher Education” in 2020, with the original title “”Existence first and then development”: A logical analysis of the actions of young liberal arts teachers in N University”,It only represents the author’s point of view and is hereby compiled for your reference.
The performance evaluation and the “promotion or leave” system make young teachers face fierce competition. Based on interviews with young liberal arts teachers and administrators of a “double first-class” university, it can be found that in the face of external challenges, teachers adopt the action strategy of “survival first and development later”.Teachers use cultural capital “efficiently”, follow “hot spots”, and actively “irrigate”. Under the pressure of “survival”, teachers pay more attention to scientific research than teaching, and have obtained the collective acquiescence of the college level.As a member of the academic community, teachers transform academic relationships into higher academic output. The academic championship system imposes huge rigid pressure on young liberal arts teachers, making them turn into rice-liang seeking; colleges and universities seek survival based on scientific research, and pass it on to teachers. The strategic behavior of peers strengthens the external motivation of teachers, and then makes them learn and imitate. It shows the interaction relationship between “institution-situation (peer, organization)-action”.
In 2018, the number of young teachers under the age of 40 in colleges and universities in my country exceeded 870,000, accounting for 53.63% of the total number of college teachers (1.63 million).As the main body of college teachers, young teachers are the most innovative group in the teaching staff of colleges and universities, and they are the new force for the long-term development of higher education. However, this group faces a huge crisis,Young teachers known as “worker bees” become “three lows”(low status, low income, low title)the pronoun.In today’s university field, the hierarchical resource allocation method, the evaluation system of quantitative competition, and the employment system of “no promotion or leave” make young teachers at the bottom of the pyramid. But at the same time, teachers are not completely passive in the face of system and organizational requirements, they will take corresponding action strategies and respond proactively. How do young liberal arts teachers deal with these challenges, what factors influence their choices, and what are the commonalities? This paper takes the young teachers of liberal arts in a university as the research object, trying to answer these questions.
▍Problem formulation and literature review
Existing studies have shown that the performance evaluation system and the personnel employment system of “promotion or leave” in recent years have had a strong impact on the professional development, academic identity, and self-identity of young teachers. In the face of a powerful system, college teachers, as actors in the field of colleges and universities, choose their actions with personal rational thinking and judgment. Hoyle and Wallace (2007) found that in the context of British curriculum reform, teachers would adopt three strategies of conformity, disobedience and reconciliation. Levin (2018) found that under the influence of neoliberalism, tenured teachers in American colleges prioritized academic logic and weakened the power of neoliberalism by adopting strategies such as adaptation, conformity, nostalgia or “like nostalgia”, disguise, sacrifice, or resistance. way to maintain their academic identity. Huang Yating (2017) found that most of the interviewed teachers in two research universities in my country were “adapters”, and most of them chose to guide their academic practice by the authoritative standards advocated by the external appointment system reform, but what type of adaptation are closely related to the teacher’s background. Yan Guangcai (2018) found that the current system design puts all-round pressure on teachers, prompting teachers to avoid research topics that are difficult, uncertain, long-term, and risky of failure, and then choose low-risk, short-term but possibly low-level research topics. Even repetitive research to improve output efficiency. From the above literature, it can be seen that in the face of the system, college teachers have different action strategies, and factors such as teachers’ professional titles, academic backgrounds, resources, disciplines, and academic relationships will affect teachers’ behavior.
In addition, the above studies are discussed under the framework of “institution-action”. Many scholars regard the evaluation, promotion, and employment system of college teachers as an academic championship system (Yan Guangcai, 2012; Lu Xiaozhong, Chen Xianzhe, 2014; Niu Fengrui, 2016; Zhong Yanpeng, 2018), and believe that this system is efficiency-first and benefit-driven. Binding national goals, organizational needs and personal goals to generate strong incentives for individuals. Some scholars have also put forward the framework of “institution-identity-behavior”. The academic system will enable young teachers to experience the process of institutional identification such as interest identification and value identification, and ultimately produce individual actions.But in fact, the teacher evaluation and appointment system does not play an independent role on teachers’ behavior, it is embedded in a specific situation, and many factors in the implementation of the system will affect the effect of the system on the individual.In daily life, as an individual’s work unit, the grass-roots organization will respond to the system, thereby generating incentives and constraints for the individual. Therefore, we cannot ignore the function of the organization in this process. On the one hand, university organizations will selectively interpret and spread the academic system at the national level, and the systems and policies formed within the organization are closely related to teachers; The degree affects the teacher’s action orientation.In the process of system implementation, if colleges and universities find that the reform violates the interests of the organization itself, they will bargain for policies, or carry out selective implementation through specific methods such as “policy above and countermeasures below”. This affects teachers’ value judgments,In addition, the attitudes and behaviors of members within the organization may also have an impact on teachers’ actions, which has not been paid enough attention to in existing research.
On the basis of the “institution-action” framework, we further pay attention to the specific situation of young teachers, and believe that the situation has an important impact on teachers’ choice of action. In addition, this study hopes to focus on the action choices of young liberal arts teachers, mainly based on the following two aspects:
1. As the main body of college teachers, most of the young teachers are at the bottom of the academic ladder, trapped in the lack of various types of capital, and are vulnerable and unstable. Therefore, paying attention to young teachers has a stronger realistic concern.
2. The liberal arts (especially the humanities) with the characteristics of accumulation and development are particularly weak under the current project-based and quantitative evaluation system. However, under the influence of academic capitalism, research on the changing nature of scholars’ work and life mainly focuses on applied disciplines with higher market value, and there are relatively few studies involving liberal arts teachers.
Therefore, this paper proposes to explore the following questions: What strategic behaviors do young liberal arts teachers in colleges and universities show when facing the demands of their daily work?What logic of action to follow? What are the factors that lead to the above strategic behavior and logic of action?
▍Research Design(excerpt)
Although teachers’ action choices are visible, the logic behind their actions is hidden, so the study uses qualitative research to dig deeper into the meaning behind the phenomenon. This research adopts purposeful sampling and convenience sampling, and selects the young teachers of liberal arts in N University as the research object. N University is a first-class comprehensive research university in China. After determining the N university, after comprehensively considering the major, employment status, professional title and other factors,With the help of independent email contact and snowballing, we selected 7 young liberal arts teachers, 4 associate deans of the college, and one deputy director of the Academic Affairs Office. The reason for selecting the latter two groups is that they represent the opinions at the department and school level respectively.(See Table 1 and Table 2).
▍The action logic and strategic behavior of “survival first and development later”
The action logic of the young liberal arts teachers of N University can be summarized as “survival first and then development”. Teacher N5’s point of view explains this logic well:
“
I heard an old professor say that you should survive first and then think about the field you like to do, so survival is the first key. The boards under your feet are all empty, and you can’t stand still, what should you do? ”
To survive, teachers take a series of specific strategic actions. Strategic behavior originates from the interaction between people in social interaction and is a rational choice. It is often related to two factors, one is to maximize personal interests; the other is to make judgments about the actions of others in advance. The strategic behavior of young liberal arts teachers in N school refers to a series of behaviors that teachers take to maximize personal performance in order to achieve short-term goals in a highly competitive environment.
(1) Weapons of the Weak: Maximizing the Utility of Cultural Capital
In the field of colleges and universities, young teachers are often at the bottom of the field. Most of them are in the initial stage of life and career, lack of social capital, weak economic capital, and most importantly, lack of professional capital,Mainly reflected in the difficulty of obtaining institutional recognition,They are undoubtedly the weakest among college teachers. However, at the same time, the young teachers of N University all graduated from well-known universities, received systematic high-level academic training, possessed the most cutting-edge knowledge and technology, and possessed a certain amount of cultural capital. Moreover, they are flexible in their minds and have no idea how to successfully transform the cultural capital in their hands. There is a logic of its own for professional capital.
1. Chase “hot spots”.
Humanities and social sciences take human spirit and social behavior as the research objects, and are closely related to the social status quo.In terms of paper publication, keeping up with current affairs not only ensures the needs of topic selection, but also satisfies the preference of journals.Respondents N2 and N3 have mentioned that teachers of this subject pursue “hot spots”.
The field of education closely follows national policies and reforms, and that kind of articles may be relatively easy to produce., some people will catch faster. (N2)
Scholars will choose topics that are easy to publish, topics that are easy to take, or hot issues to study, and ignore unpopular topics. (N3)
In terms of subject selection, it is increasingly common for university teachers to obtain scientific research funding through subject approval. Teachers in the full-time scientific research posts of N University who want to be hired as associate professors must apply for national-level project topics. The topics are usually divided into “guideline propositions” and “independent propositions”. Most of the topics included in the guideline are national preferences and market needs.In order to increase the hit rate, teachers will deliberately choose topics according to the guidelines, although this may not be in line with the teacher’s research interests. Respondent N6 said that national topics and assessments are tied together, making it difficult for teachers to pursue “leisure curiosity”, and the propositions of the guidelines are contrary to teachers’ research interests, which can easily lead to job burnout.
Teacher N1 has worked in N University for 15 years. As a “senior” young teacher, he believes that chasing “hot spots” is more likely to appear in young teachers.
I think there are actually quite a lot of young and middle-aged teachers, especially young teachers (chasing “hot spots”).
Some people will do some “hot spots” and use a way they feel is quicker to produce some results.There are also middle-aged teachers in N University, but I see older ones, such as those over 50 and 55 years old, just the older generation. I don’t think those teachers are very good at chasing “hot spots”.
Because they’re probably already there, they don’t need this thing。 (N1)
The promotion of professional titles is a battle for resources and future. Compared with the stable establishment of middle-aged and elderly teachers, associate professors are a “hurdle” for most full-time scientific research teachers.Therefore, they hope to “overcome the hurdles” by chasing “hot spots”, and then concentrate on research with long-term value after obtaining a stable “iron rice bowl”.
2. Actively “watering”.
“Irrigation” refers to faculty pursuing research speed and quantity at the expense of research quality. The current layman evaluation led by administrative power borrows statistical data such as SSCI and CSSCI to quantify the scientific research work of teachers, so that the original academic activities with rich meanings are transformed into a set of objective and standardized quantitative indicators, and educational practice is alienated into a series of endless series. In the game of reaching the standard, young teachers are “dominated by numbers” consciously “benchmarking” and actively “watering” to win by quantity.
Scientific research will lead to the phenomenon of quick success and instant benefits, which is very common.
The current assessment method only looks at papers and only the number of papers, so everyone is irritating like crazy.For us young people, it was not worth writing an article, but it was written as an article. (N7)
I think maybe one day out of this consideration, I have to do some research that I may think is average but it produces fast results, in order to cope with such an assessment mechanism. (N1)
“Irrigation” is obviously contrary to the professional aspirations of young teachers, “this kind of thing will go wrong sooner or later.” (N7) Therefore, young teachers will carry out a certain degree of “watering” within a controllable range. “Everyone is still responsible for their own academic dignity, and still cherishes their own feathers.” (N7)
But this does not mean that teachers will completely abandon their research interests and ignore long-term academic development. After reaching the standard, they will continue to work in their fields of interest. Achieving the standard ahead of time reflects the expedient measures under abnormal conditions.
My efficiency is quite high. I published 5 articles last year and completed the tasks for the next 3 years.
In the next two years, I will write whatever I want to write, and I will earn money by writing a little.(N6)
(2) Emphasis on research and less on teaching: the community of interests behind collective silence
Although young teachers are the “weight-bearers” of teaching, it is the scientific research results that really decide whether they can be promoted or not. Therefore, under limited time and energy, compared with spending a lot of energy on teaching, the results obtained are not important or difficult to measure, focusing on a scientific research field and creating considerable output is in line with the vast majority of people as “rational people”. “The Choice of Young Teachers.
The teacher is very kind to himself, but just like the students.
Research performance is their own, but teaching means nothing to them,muddle along. (N1)
But at the same time, they also issued voices such as “I really want to teach the class well, and teach the book well according to my duty” (N1), “Teaching is good, and I hope to pass on the knowledge that I have to the students” (N7).This shows that they agree in their hearts that teaching and educating people is a teacher’s duty, but it is difficult to effectively balance scientific research and teaching in practical work.These cries are more like “cries of the oppressed” than teachers’ desire to regain their vocation.
In addition, “emphasizing research and neglecting teaching” is not only a personal behavior, but also has the tacit approval of colleges and universities. They encourage teachers to engage in scientific research and “turn a blind eye” to the behavior of “despising teaching”.
Because if the school does not pay attention to the scientific research of teachers, the social influence of the school will decline, the social influence will decline, and the quality of students will decline. The whole is a vicious circle.Therefore, schools must pay attention to the scientific research output of teachers. Naturally, more than 50% of teachers’ energy must be devoted to scientific research. “(T1)
On the one hand, colleges and universities need the high productivity (scientific research) of teachers to improve the prestige of colleges and universities, and on the other hand, teachers need obvious scientific research achievements to be promoted. The two hit it off and form a community of interests. thus,Institutions have fallen into collective silence about the under-investment of teachers in teaching, which has allowed the practice to occur widely and repeatedly.
(3) “Holding the Thighs”: The Rational Transformation of Social Capital
Social capital is the social structural resources obtained by acting on the social relationship network based on trust, and it is an important force affecting the achievement of individual instrumental behavior goals. In the early stage of career development, young teachers have limited ability to accumulate social capital and lack of social capital stock, so tutors have become their important social capital, and tutors have given young teachers a lot of help in terms of paper publication, project approval, and participation in conferences. The use of social capital relies on the trust and norms of established academic relationships, in exchange for the effective improvement of academic status.
Some of the young teachers I know have published articles such as a dozen or so, right?
Some of them are of course cast by their own abilities, but some are really because he has a close relationship with the editor, or the tutor helps to contact and communicate. and attending academic conferences.The circle of tutors is wider than that of young teachers who have just graduated, so if the tutor gives you a tip, you can go to the academic conference. (N5)
In addition, some teachers actively expand overseas relations, strengthen international cooperation, take an advantageous position in the publication of papers, and obtain institutional recognition as soon as possible, but such cooperation is often an instrumental rational behavior.
Many people have told me that when you go to study abroad for a year, you know one or a few top people in this field, then you can post articles with him after you come back, and you can quickly learn in China.You can send some English, because now the proportion of English journals is not larger. This kind of cooperation at this level is not to promote the exchange of disciplines, it may be a little complementary, right? But fundamentally it may be for the sake of better performance, I think this is different. (N1)
▍Cause analysis of the action logic of “survival first and development later”
The action logic and strategic behavior of “survival first and development later” proposed in this study is not only the behavioral orientation of individual young teachers, but also the behavioral orientation of individual young teachers.Presenting an informal state of collective action. This is different from the moral pursuit that teachers should abide by, so it mostly occurs in an informal form; in addition, once such behavior is rewarded accordingly, individuals will use others as a reference and rationalize themselves, causing mutual imitation in the teacher group. Rising to a collective action, since it is understood as a non-individual behavior, it should abandon individual differences and explain it from a broader perspective. The “institution-action” framework certainly provides an important reference for us to explain the action choices of actors, but at the same time, the situational factors during the implementation of the system may influence the action orientation of actors. This study believes that the rigid pressure exerted by the evaluation and appointment system of the “Promotion Championship”, the demonstrative force derived from peer behavior, and the organization’s intentional guiding force, all three forces together promote the formation of “first survival” among young liberal arts teachers. post-development” action logic (see Figure 1).
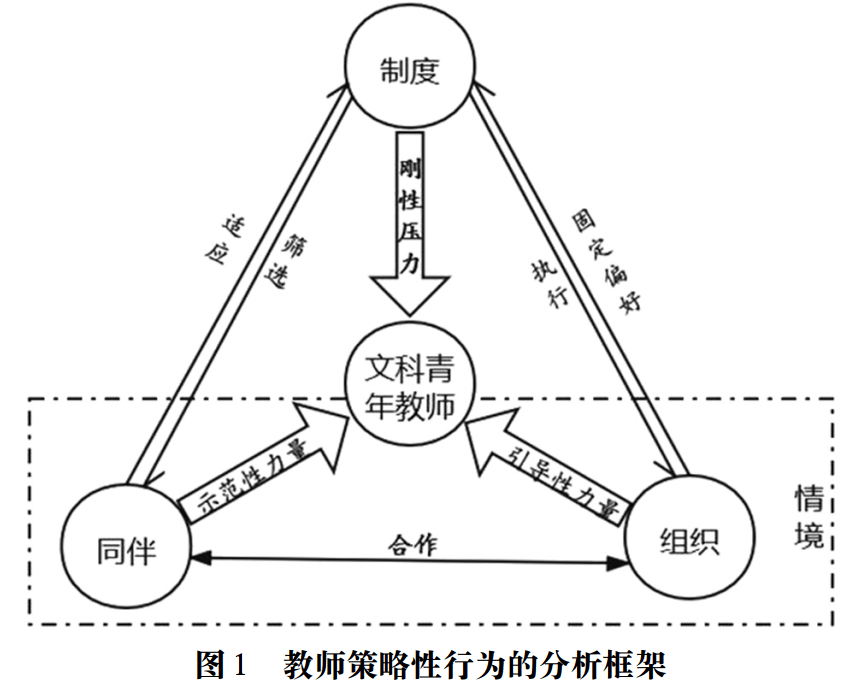
(1) Rigid Pressure: Survival in the Cracks of the Promotion Championship
As a relatively objective and stable incentive mechanism, the teacher evaluation system of N University promotes the steady increase of the academic output of N University and ranks in the forefront among “double first-class” universities, but at the same time, the characteristics of “promotion championship” are given to young teachers of liberal arts. Huge rigid pressure. The tournament system has the following characteristics:
First, it is highly quantified. For the convenience of calculation and comparison, it quantifies teachers’ teaching, scientific research, and social services into specific scores. This “number worship-style” evaluation standard essentially adopts a positivist way of thinking, which is scientific in form and irrational in nature for the liberal arts, especially the humanities.
Second, promotion competition. Although the assessment numbers are deterministic, teachers are bound by uncertain absolute performance indicators. In other words, whether young teachers can be promoted depends on the relative ranking of the competition results, not the absolute performance. In order to win the limited establishment, teachers must rank better than others.
Third, the external incentives of high reward and high punishment. The evaluation system places young teachers who care about promotion under strong incentives. First, the results of the assessment are closely linked to teachers’ remuneration, employment, and rewards, so the evaluation system has a substantial distribution function. Second, this resource distribution has the extreme characteristics of “high rewards and high penalties”. Full-time scientific research teachers who are successfully promoted to associate professors during the employment period enjoy corresponding treatment, and the formal establishment of professional capital brings them a series of development opportunities.
Yan Guangcai (2018) once pointed out that the function and function of the system are brought into play by mobilizing the cognition and emotion of the recipient, and mediated by an individual can feel the pressure, thereby promoting a collective consciousness and action strategy. The championship system imposes all-round rigid pressure on young liberal arts teachers, including pressure to meet standards, pressure to compete, and pressure to eliminate “if you don’t get promoted or leave”, etc. These work pressures are accompanied by economic pressures and life pressures, so that young teachers can only keep running forward without a breath. Respondent N7 said that the full-time scientific research post teachers are non-staff personnel, and it is difficult to “enter the staff”.The existential stress of job uncertainty serves as a trigger for other sources of stress.Moderate pressure can keep teachers’ research vitality, but once the pressure threshold is exceeded, and individuals cannot cope with the pressure on their own,It is very likely to take some strategic actions, showing action choices that conform to instrumental rationality but not value rationality.
(2) Guiding power: hints and transmissions within the organization
In my country, the government uses administrative orders, policies and regulations, and financial appropriations to dominate the resource allocation and hierarchical order in the field of higher education. Therefore, the state-led institutional arrangement is in an advantageous position in practice, and colleges and universities are in a relatively weak and subordinate position. The system design needs to be highly coincident with the national will. But in fact, the policy texts formulated by colleges and universities cannot truly and completely reflect the values of colleges and universities. Colleges and universities will selectively implement them based on the consideration of organizational interests. Some policies are faked and other policies are strengthened. A signal that guides it to make a choice of action.
In recent years, the Ministry of Education has proposed “breaking the five wickedness” to promote multi-dimensional and multi-level evaluation of teachers, especially highlighting the assessment of teaching performance and teacher ethics. In 2017, N University promulgated the “Interim Measures for the Implementation of the Employment of All Staff of N University”, which pointed out that teachers should be comprehensively assessed and evaluated, which not only reflects the unit’s own requirements, but also promotes the professional development of teachers.This shows that the teacher evaluation and employment system of N University are highly consistent with the national requirements.“In the middle of the implementation process, the school couldn’t make up its mind.”(T5) Teacher evaluation is simplified to piece-based evaluation based on scientific research, and the developmental function of evaluation is neglected, showing selection and reward and punishment.
This is because the country’s policy goals are relatively parallel and focus on both. However, for colleges and universities, the indicators are not necessarily compatible with each other, or it is difficult to fully take into account within a certain period of time. Therefore, as a rational organization, colleges and universities will Take selective actions according to their own goals, action efficiency and benefit evaluation, rearrange the sequence of policy goals, and ensure that important goals are prioritized. Some scholars pointed out: “Educational organizations formulate a large number of rules that have legitimacy, but are only willing to disseminate those rules that are proven to be efficient.” Among N universities, scientific research, as the most revealing indicator, is of great significance for building a first-class university. ,
“I once interviewed the director of the Academic Affairs Office, and he said, ‘In a university like N, it is unrealistic to mention that teaching is more important than scientific research. As a research university, the primary task of N University is to support innovation, so teachers must engage in scientific research. ‘”. (T3)
In the specific assessment process, N University consciously strengthened the requirements for scientific research, increased the code layer by layer, implemented “one-vote veto” for those who did not pass the scientific research, weakened teaching,The teaching requirements are only the passing line, not a hard lever. “As long as you are excellent in scientific research, the defects in teaching can be covered up and can be accommodated.” (T5)
Organizational attitudes and action choices directly affect teachers’ judgmentsIn practice, teachers have become “assessing the situation”, “weighing the pros and cons”, clarifying their primary goals, and “focusing” their work on coping with various quantitative inspections and assessment activities.
(3) Demonstrative power: observational learning and imitation among peers
The action choices of young teachers are affected by long-term peer interaction. Young teachers make their own rational judgments by observing their peers’ attitudes and reactions to the system. Unlike traditional behaviorism, which believes that learning is based on practical experience, Bandura believes that a more important, universal, and effective way for humans to learn is observational learning, which reduces the risk of trial and error. The same is true for young teachers in colleges and universities. Those who fail to meet the standards during the two employment periods (6 years) face the cruel “promotion or leave”.In fact, under the condition that the flow system of teachers in colleges and universities in our country is not perfect, the young teachers who are eliminated are easily labeled as “unqualified” and “low-capacity” and other derogatory labels, and there is a failure of downward mobility, which makes them dare not easily adventure,More willing to stay in the school to observe the experience of peers and explore the way of promotion.
In addition, Bandura divides observational learning into four processes: attention, retention, action reproduction, and motivational processes. Observers choose, abstract and generalize their behaviors by observing the demonstration prototypes, and store them in memory in a symbolic way. When the motivation is strengthened, they produce imitative behaviors. First, young teachers tend to observe the behavior of teachers of their own age and ability level, and if they exhibit the above-mentioned strategic behavior, they will take it to heart. However, observation does not necessarily lead to imitation. It must be transformed into motivation before further imitation. In other words, motivation becomes an important bridge between knowledge and action in imitation. Motivation is largely affected by the action results of the observed. If other young teachers who adopt strategic behaviors do not receive organizational punishment, but instead get promoted quickly, this will stimulate the motivation of teachers to imitate, and then produce imitative convergence behaviors.
Everyone has to compare. Seeing that they were distributed with me, Zhang San bought a house, and Li Si bought a car. Why? People publish C journals, and then get major projects, (various rewards), and I will teach every day, and I will not be able to evaluate my professional title in the end, right? (T4)
If I was a very serious and responsible teacher, I did well in class, I spent a lot of time in class, students like it very much. But I found out that the people around me are not doing well in class, he may do scientific research well, or make good money outside,
Then when I see this phenomenon, my heart will be out of balance.Because I invested so much, I didn’t get any reward, and it was still difficult to evaluate the title. In such a situation, a thought may arise: Since you do this, why don’t I do it? (T2)
In addition, there is a relationship between the system and the situation (partners, organizations), and the implementation of any system cannot be separated from the specific implementation process. Specifically, the first is the relationship between the system and the organization. Colleges and universities use the policy text of teacher evaluation to fix their preferences, refine and transmit the “double first-class” goal to individual teachers, and establish a direct connection between teacher performance and the “double first-class” goal. The purpose of the teacher evaluation system is to mobilize teachers’ enthusiasm for work and increase academic output, but whether the policy goal can be successfully achieved depends on the organization and mobilization ability of colleges and universities in the process of policy implementation. The second is the relationship between the system and peers. The teacher evaluation system hopes to select “mature academic individuals” in a short period of time. Under this system, all teachers will be compared, graded, ranked, rewarded and punished, and the successful ones will finally be selected. Under the evaluation system, teachers also show different differentiation. As a special group, young teachers may or may not agree with the system, but they are unable to change the status quo and can only follow the rules.Young teachers who are successfully promoted are more likely to actively maintain this system, which directly affects the action choices of other young teachers.The last is the relationship between the organization and its peers. The organization includes both administrators and academic communities. Teachers are important members of the academic community. Teachers and administrators also need to support and cooperate with each other.
▍Conclusion and Discussion
The study found that the young liberal arts teachers of N University showed the action logic of “survival first and then development”. As high-level intellectuals, they operated the cultural capital in their opponents “efficiently”. and other methods to meet the assessment requirements; as individuals in the administrative organization of colleges and universities, teachers pay more attention to scientific research than teaching, and have obtained the collective acquiescence of the college level; as a member of the academic community, teachers actively use social capital and rationally transform it into academic achievements. This article explains the above behaviors by constructing an analytical framework of “institution-situation (peers, organizations)-action”.The “promotion championship”-style academic system imposes huge rigid pressure on young teachers, and liberal arts teachers are particularly vulnerable. Young liberal arts teachers who are on the edge of “going” and “staying” have to seek for Daoliang;In the implementation of the system, colleges and universities intentionally “overweight” scientific research, weaken teaching, and pass on the “scientific research-oriented” survival method to teachers, and then guide young liberal arts teachers to continue to benchmark and meet the standards; the strategy of high rate of return for peers Sexual behavior strengthens teachers’ external interest motive, which makes them learn and imitate, and promotes the process of teachers’ professional socialization. The superposition and joint action of the above three factors make the action logic of “survival first and development later” inevitable.
This study also raised the following thoughts.
First, the “system-action” relationship is an important topic in institutionalist research. The system contains incentives for interests (material and spiritual) and punishment for violations, and there are corresponding adjudication and enforcement mechanisms. Any teacher will weigh whether to comply with or violate the system. the pros and cons before making a rational choice. Existing studies have found that the “adaptation and compliance” shown by young teachers in front of the system is precisely the normative role of the system. The researchers do not try to overthrow this assertion. On the contrary, this judgment has strong applicability, but in the case of N University, the researchers found that the important factor of context also affects teachers’ value judgments and action choices. This is because the interaction between institutions and actors does not take place in a vacuum, but occurs in specific scenarios and situations, and many elements in the process of institutional implementation will affect teachers.
Second, the action judgment of “survival first and then development” made in this study has the same meaning as “obedience” and “adaptation” shown by teachers in previous studies, but there are also differences.“Surviving first, then developing” is not blind obedience and completely mechanical compliance with external requirements, but has a more flexible and developmental meaning. The long-term development needs of teachers after the survival problem is solved cannot be ignored.However, for teachers, young teachers who are at the peak of their creativity do not devote themselves to long-term valuable research, but rack their brains to publish “short-term and fast” academic achievements, which can easily damage teachers’ lofty mission of “taking academia as their career”. It is detrimental to their long-term academic development. For the teaching team, it is easy to cause reverse elimination, which is not conducive to the improvement of the overall quality of the teaching team.
Third, the above action logic and strategic behavior cannot simply be attributed to the lack of teachers’ personal professionalism. Why it happened and evolved into an informal collective action is an unintended product under the combined effect of the system and the situation.This helps us understand that the resistance to a series of reforms in current practice, such as teacher evaluation, employment, and assessment, is to some extent an organizational problem and a system problem, which affects the whole body.
This article was originally published in the 7th issue of “Exploration of Higher Education” in 2020, with the original title “”Existence first and then development”: A logical analysis of the actions of young liberal arts teachers in N University”,Personal sharing is welcome. For media reprints, please contact the copyright owner.Return to Sohu, see more
