Prevention is the best weapon to win cancer. Undergoing regular check-ups and diagnostic tests allows you to identify the neoplasm at a very early stage and treat it effectively, obtaining a greater number of recoveries it’s a reduction in the mortality rate. Here, therefore, what checks to do in each age group to prevent or promptly diagnose tumors.
Exams and visits for girls under 25
Girls under the age of 25 should undergo the first gynecological examination with possible pelvic ultrasound. It would be better to do it already “during adolescence, at a time of hormonal change”, he says Rossella Nappiprofessor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Pavia, who disclosed some advice on female intimate well-being in collaboration with Meclon Lenex, Alfasigma cosmetics.
Furthermore, the specialist suggests carrying out «the vaccination of the human papilloma virus, known as HPV, recommended and free for girls and boys aged 11 and over. It is an infectious virus of which over 200 variants (serotypes) are known: in some cases it can cause warts and warts, in others the infection can lead to cellular changes that slowly progress into tumor forms of the female reproductive system affecting the neck of the uterus, but also the vagina and vulva, as well as other organs and contact systems”.
Tumors: checks to be done in the age group between 20 and 40
Exams for her and for him
Both sexes should check moles, because this is the best prevention against melanoma. Mole control must be done periodically, independently, following the procedure ABCDE rule.
«The A stands for asymmetries: generally moles are symmetrical and it is possible to draw an imaginary line that divides them into two equal parts; suspicious moles, on the other hand, are made up of two different halves. The B stands for edges: those of an anomalous mole, which could degenerate into melanoma, are irregular, jagged, toothy. By C we mean the colour: a mole that is particularly dark or has non-homogeneous shades that turn red, pink or blue must be scrupulously checked. The D stands for size: atypical moles are larger than six millimeters. Finally, by E we mean the evolution: it is necessary to monitor all the changes in the appearance of a mole, especially if these occur in a short period of time, i.e. approximately 6-8 months”, he explains Elisabetta Sorbellinispecialist in dermatology and venereology and owner of Studio Sorbellini in Milan
As suggested by the LILT National Commission, if suspicious pigmented lesions are found it is best to undergo treatment immediately dermatological examination for an accurate diagnosis. The specialist proceeds with one mapping of moles by dermatoscopy (or epiluminescence)which is a non-invasive and painless technique that allows you to examine the dermis, epidermis and other layers of the skin to identify any anomalies.
It is the dermatologist who establishes the frequency with which the mapping should be carried out. In general, anyone should have a dermatoscopic examination at least once in a lifetimebetter in autumn or winter because the skin is not tanned and the specialist can carry out a more accurate analysis.
Exams for her
Gynecological examination. The gynecologist will check the objective conditions of the external genitalia, to check whether they are red or inflamed, and during the visit it will also be possible to ascertain whether the patient experiences pain at the entrance to the vagina. Then she will investigate the state of the cervix (looking for fibroids and areas of tenderness), the ovaries and the tubes. A gynecological examination should be done at least once a year.
Pelvic ultrasound: this is an absolutely harmless investigation, but valuable for viewing the organs contained in the lower abdomen, especially the uterus and ovaries, and to flush out the presence of malformations or atypical masses. It should be done at least once a year after the start of sexual activity and in preparation for pregnancy.
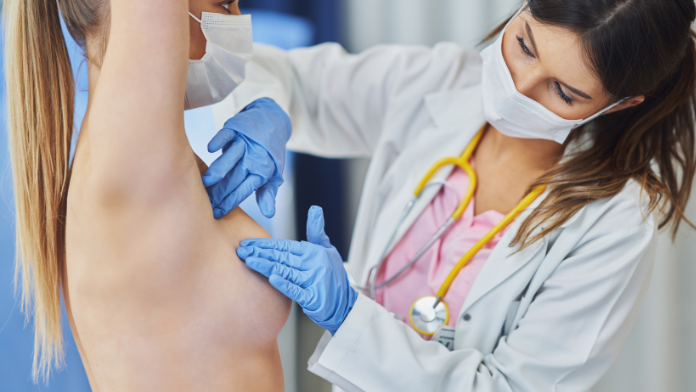
Breast self-examination: it is a test that women can perform alone from the age of twenty, once a month or every two months.
Breast ultrasound: is the examination of the breast through ultrasound. It must be done once a year from the age of 30. In patients with two close family members affected by breast cancer, ultrasound should be combined with mammography from the age of 40.
Pap test (or vaginal smear): «not to be overlooked, the Pap Test is a screening test that is best done on a regular basis every 3 years or based on your risk and which allows you to detect anomalies
pre-tumor or tumor», continues the gynecologist Rossella Nappi.
Exams for him
Self-examination of the testicle. I testicular tumors represent one of the leading causes of mortality from neoplastic pathologies in young males. But they are also the most curable, if caught in time. And self-examination is certainly a very valuable aid in detecting these anomalous presences early. It must be performed periodically.
Tumors: the checks to be done daged 40 and over
Exams for her and for him
Prevention of colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancers represent the third most common cancer in men and the second most common in women. The report says so Cancer numbers in Italy 2023. The good news is that 90% of malignancies in the large intestine derive from a precancerous lesion, the transformation of which takes approximately 10 years. Here, then, is the invitation to carry out the following revealing tests:
Fecal occult blood test. The current guidelines require that all healthy individuals between the ages of 50 and 69 (in some regions up to 74 years of age) begin to undergo fecal occult blood testing every two years and at the invitation of their local ATS. Positive cases will require further investigation through a colonoscopyto confirm the suspected diagnosis.
Exams for her
Gynecological examination and pelvic ultrasound: essential for evaluating the state of the uterus and ovaries in premenopause, menopause and post menopause. The gynecologist may also prescribe hormone replacement therapy to mitigate the woman’s symptoms when ovarian function fails. The visit should be done every year, while the ultrasound should be performed at a frequency established by the gynecologist. However, «we don’t have to wait
the annual appointment if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge, abdominal pain or swelling, pain during sexual intercourse or changes in your menstrual cycle. In these cases it is best to contact the gynecologist immediately”, continues Nappi.
Pap test. When it is normal, it is sufficient to repeat the survey once every 3 years.
Breast self-examination: every 1-2 months.
Breast ultrasound: first level exam in women up to the age of 40, remains an excellent diagnostic ally hand in hand with mammography even after. It must be done every year.
Bilateral mammography: consists of an x-ray of both breasts. It is recommended from the age of 40, every two years, and every year after the age of 50.
Exams for him
Self-examination of the testicle. The habit that should be followed as a teenager should not be neglected even after 40. It should be done periodically.
Prevention of prostate cancer. 75% of prostate tumors it is diagnosed in the over 65 age group. If diagnosed in time, it is a highly curable tumor. Here is a triptych of tests that most international scientific societies recommend carrying out once a year starting from the age of 50:
Clinical visit with rectal examination: it is the first, elementary, but crucial control of the prostate gland.
PSA assay. From a blood sample, the values of a substance called prostate specific antigen (PSA) are examined, an increase in which in the blood could indicate the presence of a tumor.
Transrectal echography: it is a technique that uses ultrasound, thanks to a thin probe sprinkled with lubricating gel introduced into the rectum.