El Niño Phenomenon Expected to Cause Extreme Weather and Record Temperatures
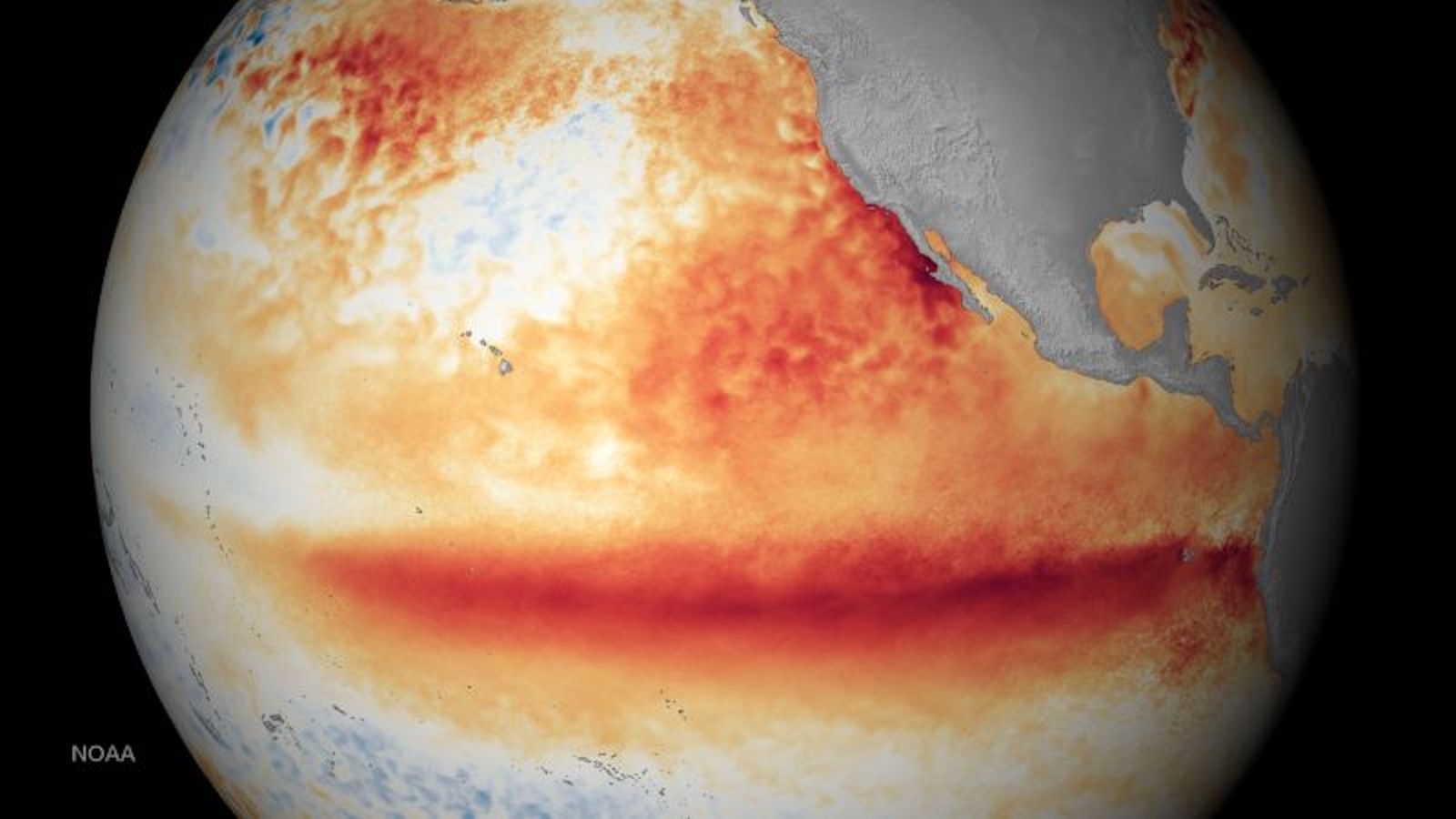
(CNN) – The World Meteorological Organization has declared the beginning of the El Niño warming phenomenon, warning governments to prepare for more extreme weather events and record temperatures in the coming months. El Niño, a natural weather pattern in the tropical Pacific Ocean, brings warmer than average sea surface temperatures and has a major influence on climate worldwide.
El Niño occurs every two to seven years in varying intensity, with the eastern Pacific experiencing temperatures up to 4 degrees Celsius warmer than normal. A strong El Niño warms the atmosphere and changes circulation patterns, especially the jet stream over the Pacific. This leads to stronger and more frequent storms in the western US, particularly in California, and more rain for the west coast of South America.
However, this weather pattern is a zero-sum game. While North and South America experience increased rainfall, normally rainy regions in South Asia and Australia suffer from droughts. El Niño has also caused intense flooding in eastern Africa, leading to landslides, waterborne diseases, and food shortages. Furthermore, a strong El Niño affects cyclone seasons globally, with more hurricanes or typhoons forming in the Pacific and fewer developing in the Atlantic due to increased upper-level winds.
The impact of climate change on El Niño remains a subject of debate. Some research suggests that while the frequency of El Niño occurrences is unlikely to increase, the likelihood of a “Super El Niño” doubles. Climate change could exacerbate El Niño’s effects, particularly in terms of extreme precipitation, which can result in devastating flooding.
On July 4, 2023, the World Meteorological Organization declared the beginning of El Niño and warned of record temperatures and extreme heat in the upcoming months. It coincides with the highest global temperature ever recorded, reaching 17.18 degrees Celsius. Experts predict that this record could be broken several more times this year, highlighting the rapid warming of the planet and the overlap between El Niño and climate change.
Governments around the world are urged to establish early warning systems and prepare for disruptive weather events. The UN emphasized the need to limit the impacts of El Niño on health, ecosystems, and economies. The World Meteorological Organization projects a 90% chance that El Niño will continue through the second half of 2023 at moderate intensity.
The past three years have been some of the warmest on record, even with the sister phase of El Niño, La Niña, characterized by colder-than-average ocean temperatures. As El Niño intensifies, it is crucial for governments and communities to take proactive measures to mitigate its effects and protect lives and livelihoods.
By Helen Regan