Astronomers Discover New Type of Star Nicknamed “Smoking Gun” in Milky Way
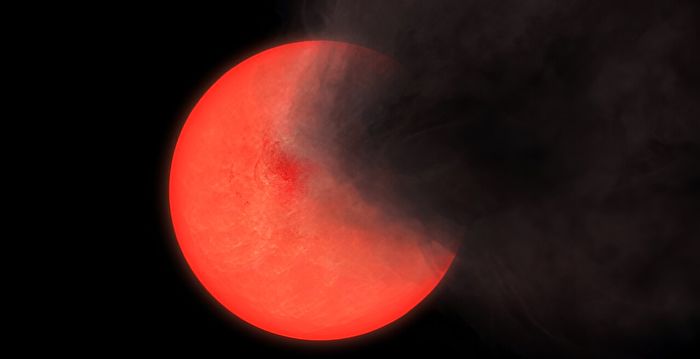
The center of the Milky Way has revealed a surprise for astronomers with the discovery of a new type of star. According to a report by The Epoch Times on January 29, 2024, astronomers have found ancient red giant stars that they have nicknamed “old smokers” due to the plumes of smoke they emit.
The discovery was announced by the University of Hertfordshire in the UK, where an international research team led by Philip Lucas, professor of astrophysics at the school, made the groundbreaking finding. These new stars, which had never been seen before, were found hidden in the center of the Milky Way and have been noted for their unique behavior.
Lucas described how these stars can sit in place for decades, slowly dimming to almost invisibility, and then suddenly puffing out plumes of smoke that obscure them from view. This behavior, never before observed in red giant stars, has left scientists puzzled as to the cause.
During their 10-year research, the international team, which included researchers from the United Kingdom, Chile, South Korea, Brazil, Germany, and Italy, observed approximately 1 billion stars through the Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy in Chile. This extensive study led to the discovery of not only the “old smoker” stars but also 32 rare, newly born stars called protostars, which undergo Big Bangs as part of the formation of new star systems.
Most of these newly discovered stars are hidden in the vast mass of dust and gas in the Milky Way, making them invisible to visible light. However, the use of infrared light allowed scientists to detect them for the first time.
The research team’s findings, which were published in the British “Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,” have the potential to change our understanding of how elements are distributed in space. Material ejected from these ancient stars plays a key role in the formation of the next generation of stars and planets, according to Lucas.
The discovery of these “smoker” stars and protostars is a significant step forward in our understanding of the universe, and it could lead to further groundbreaking research in the field of astronomy.