The case in summary:
Expand/minimize fact box
- Gonorrhea cases in Norway have increased sharply, especially after the pandemic, with almost 3,000 cases registered last year, an increase of approx. 40% from the previous year.
- Senior doctor Åse Haugstvedt expresses concern that the medicine against the disease may stop working, as many countries are struggling with gonorrhea bacteria that have developed resistance to antibiotics.
- Only one type of medicine, ceftriaxone, remains effective against the disease in Norway.
- Gonorrhea is highly contagious and can lead to painful infections and infertility, with the most vulnerable groups being those under 30, and men who have sex with men.
- Experts encourage more condom use and frequent testing, as many people can have the infection without noticing symptoms.
- Infection tracking will be important to break the chain of infection going forward, but many patients find it embarrassing to inform about their infection.
The summary is made by an AI service from OpenAi. The content is quality assured by NRK’s journalists before publication.
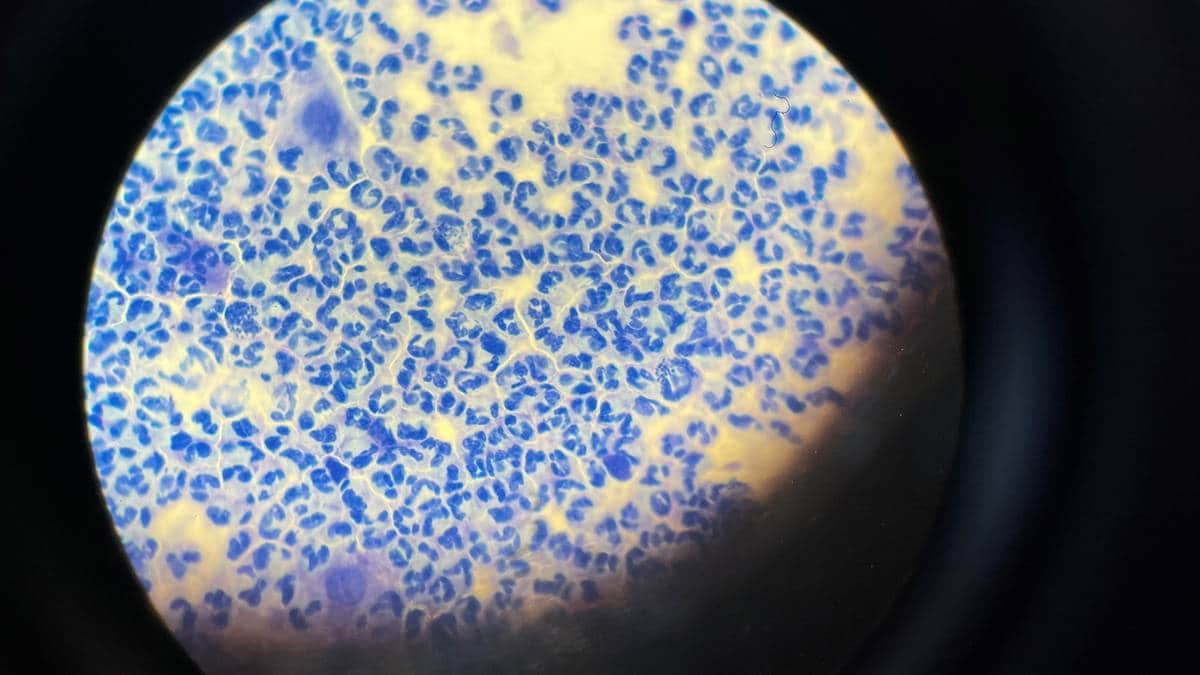
– Look here! The gonorrhea bacteria are like small coffee beans inside these cells.
Senior doctor Åse Haugstvedt points to a microscope picture.
Gonorrhea infection was very rare in Norway 20 years ago.
But particularly after the pandemic, venereal disease has increased sharply.
The Norwegian Institute of Public Health registered around 3,000 cases last year. This was an increase of approximately 40 per cent from the previous year.
January and February this year show a further increase.
– It looks like it continues. So far in 2024, there are over 600 cases nationally. It is very disturbing if it continues like this, says Haugstvedt.
She has worked with sexual health at the Olafia Clinic for 20 years.
Åse Haugstvedt is a senior physician at the Olafia Clinic, and has worked with sexual health for over 20 years.
Photo: Espen Bierud / NRK
- Recently, NRK told about a testing center for sexually transmitted diseases in Kristiansand, which is experiencing a fivefold increase in gonorrhea cases.
The medicine may stop working
In Oslo, specialist Åse Haugstvedt is worried.
Many countries, including major Western European countries such as Spain and France, are now struggling with gonorrhea bacteria that have developed resistance to antibiotics.
– It makes me very worried. People travel a lot, have sex on holiday, and come home from, for example, Thailand. It is easy to get a resistant gonococcus back in your suitcase.
The bacterium has gradually become resistant to several types of antibiotics that previously suppressed the disease.
The medicine has simply stopped working.
Now only one type remains.
– It’s starting to get really troublesome. Now we really only have one good medicine left, which we use in Norway.
The medicine is called ceftriaxone, and must be given by injection.
– So, they get an injection in the buttock, explains the doctor.
Infection tracking is important when it comes to gonorrhea, says Åse Haugstvedt, senior physician at the Olafia Clinic.
Photo: Espen Bierud / NRK
But even that injection in the butt can’t save everyone.
The first case of gonorrhea infection that could not be cured by this medicine was detected in Japan in 2009.
A few years later, the same thing happened in France, Spain, Australia and Singapore to name a few, according to Oslo University Hospital.
In 2018, the first case of this type of gonorrhea was also found in England, reported BBC.
This means that, as of today, there is no medicine that can help people with that type of gonorrhea.
They have to live with infections in their bodies.
– Embarrassing to say
Gonorrhea is highly contagious and can lead to painful infections and infertility.
The disease can be transmitted through, among other things, unprotected sex, kissing and oral sex.
The most vulnerable groups are those under 30 and men who have sex with men.
The experts encourage more condom use and frequent testing. Many people have the infection without noticing any symptoms.
It is also not certain that the infection will show up on regular tests.
– If you have been in contact with someone with gonorrhea, then everyone should get their throat tested. We see some who have negative samples, until we get them tested in the throat.
The head doctor also says that infection tracking will be very important in order to break the chain of infection going forward.
– I think that when it comes to chlamydia, it was very easy for the patients to speak up themselves. But now it seems that they think it’s very disgusting and embarrassing, so they don’t dare speak up. So then the health personnel have to be on the pitch and do that job for them.
– And you do?
– At least we do the best we can.