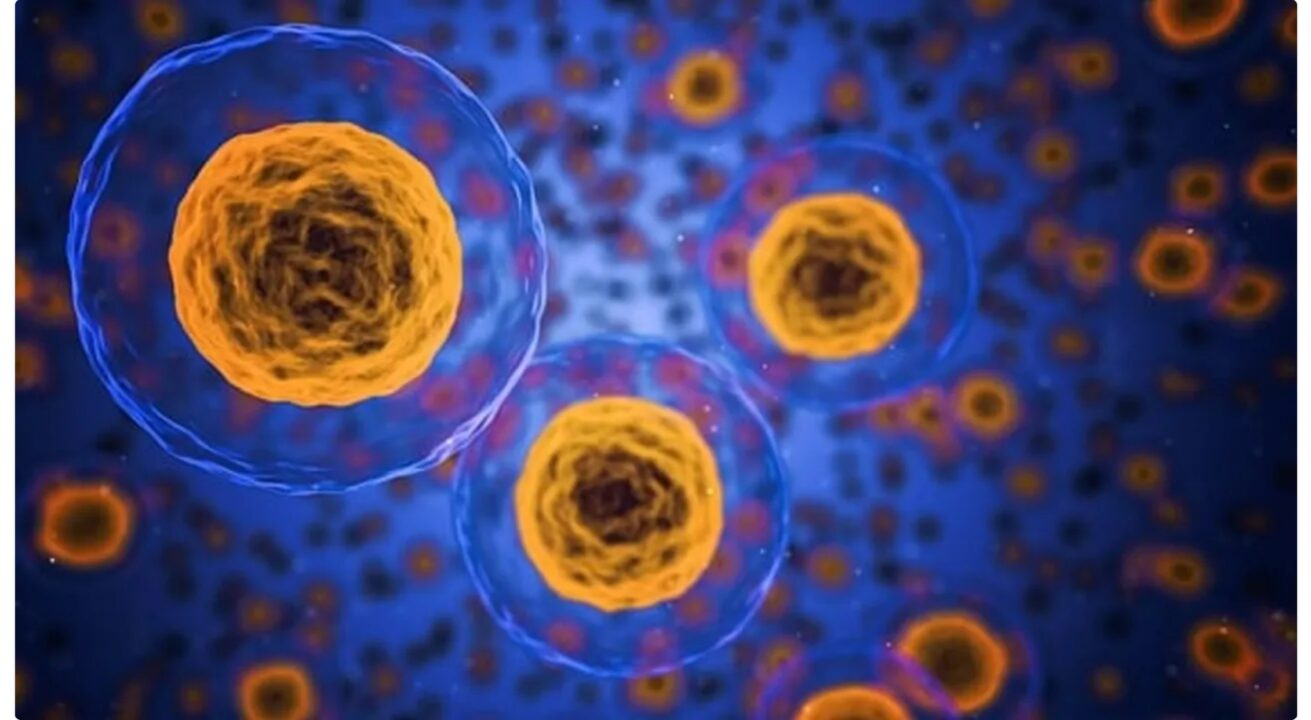
Light-activated molecular machines used to control cellular activities promise innovative treatments for heart and digestive disorders
According to a recent study, scientists at Rice University have used these “machines” that use molecules to induce intercellular calcium wave signals, opening the possibility for innovative treatments for heart, digestive and more ailments. Cells communicate with each other through signals composed of calcium molecules, to coordinate vital functions such as muscle contraction, neuron firing and immune activation. In the past, drug design relied on chemical binding forces, but this new discovery shows that it is possible to use the mechanical force generated by light-activated molecular machines. The molecular machines spin when stimulated by light, inducing a calcium signaling response in smooth muscle cells. This technology could allow for targeted, tunable control over heart function, improving the treatment of arrhythmias. Furthermore, it could be used to activate specific muscles without the use of chemical interventions.
The octopus experiment
An interesting aspect of the study was the use of molecular machines to control the whole organism of a freshwater polyp. This is the first time a molecular machine has been used to influence the functioning of a complete living organism. The cellular response was variable according to the intensity and type of mechanical stimulation. Molecular machines that rotated in a specific direction generated intercellular calcium wave signals, while slower speeds or multidirectional rotations did not have the same effect.
What makes molecular machines so promising is their mechanical action at the molecular scale. They rotate at incredible speeds and can be adjusted in terms of the duration and intensity of the light stimulus, allowing precise spatio-temporal control over cellular communication. In addition to drug design, they could be used to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria, cancer cells and pathogenic fungi. Scientists are working to develop molecular machines with improved penetration depth.
Prices: increasing in Croatia after the adoption of the euro
Air strike of 15 July: here are the guaranteed flights and those that will not leave
Artificial Intelligence: Rai Cinema participates in the Scuola Holden project
LTT9779b: Exoplanet covered in metallic clouds defies scientific theories
James Webb Space Telescope: a year of space surprises
Alien technology found on Earth?