Author: Huang Dazhi, researcher at Xingtu Financial Research Institute
On September 15, the four major state-owned banks, including China Construction Industry and Agriculture, lowered their deposit rates to varying degrees. Such as China Construction Bank, according to its official website, the 3-month, 6-month, 1-year, 2-year, and 5-year fixed deposit interest rates have been reduced by 10 basis points, and the adjusted deposit rates are 1.25%, 1.45%, 1.65%, 2.15 %, 2.65%; the 3-year time deposit rate was reduced by 15 basis points to 2.60%; the demand deposit rate was reduced by 5 basis points to 0.25%.
Since the beginning of this year, bank deposit products have received more and more attention, and the reduction of deposit interest rates by the four major banks this time has once again attracted widespread market attention. From the previous small and medium-sized banks taking the lead in lowering the deposit interest rate to today’s large state-owned banks, why are the deposit interest rates that have remained unchanged for many years now lowered? Will it continue to decline in the future? What profound impact will it have on banks, depositors, and capital markets?
1
The adjustment of bank deposit interest rates has always been a major event. At present, domestic household savings deposits are as high as 80 trillion, which means that a 10BP reduction in deposit interest rates will reduce residents’ annual interest income by at least 80 billion yuan in the future. Therefore, compared with bank loan interest rates, Deposit rate adjustments are less frequent and more impactful.
Although the interest rate of large-denomination certificates of deposit has been adjusted several times in the past two years, the comprehensive adjustment of the deposit interest rate can be traced back to the adjustment of the benchmark deposit interest rate by the central bank in October 2015. After a lapse of seven years, why did the bank comprehensively adjust the deposit interest rate again?
Judging from the changes in the deposit market since the beginning of the year, it is already imperative for major banks to cut deposit rates across the board. In “Deposit interest rates continue to fall, how should investors respond? “In the article, we mentioned that in the case of small and medium-sized banks taking the lead in reducing deposit interest rates, and LPR continues to decline, it is inevitable for banks to reduce the cost of debt by reducing deposit interest rates.
So let’s first look at why this inevitability exists. From the perspective of the bank’s business model, the return on assets and the cost of liabilities mainly determine the bank’s income and costs, respectively. On the asset side, the bank’s loan interest rate has continued to decline. Since the beginning of the year, the 1-year LPR interest rate has been lowered twice, and the 5-year LPR interest rate has been lowered three times. During the year, the 1-year and five-year LPR interest rates have dropped by 15BP and 35BP respectively. The interest rates of both short- and medium-term loans and long-term mortgages have continued to decline, which has led to a rapid decline in the bank’s asset-side yield. For example, China Merchants Bank, the “top student” among listed banks, saw its return on interest-earning assets drop by 11BP in the first half of the year. Other banks with a lower proportion of retail loans also saw only a lot more decline in their asset-side yields.
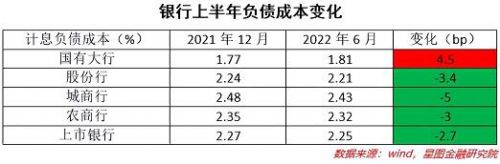
However, from the perspective of the performance of the bank’s liability side, the decline in its cost is far lower than the decline in the asset side, or even increased. Specifically, in the first half of the year, the cost of interest-bearing liabilities of large state-owned banks bucked the trend and rebounded by 4.5bp, while the average cost of interest-bearing liabilities of joint-stock banks, city commercial banks and rural commercial banks fell by 3.4bp, 5bp and 3bp respectively. If the structure of the cost of interest-bearing liabilities is further broken down, it can be seen that the deposit cost of major banks has even risen. Corresponding to the 11BP decrease in the yield of interest-earning assets of China Merchants Bank in the first half of the year mentioned above, the cost ratio of its interest-bearing liabilities increased by 3BP.
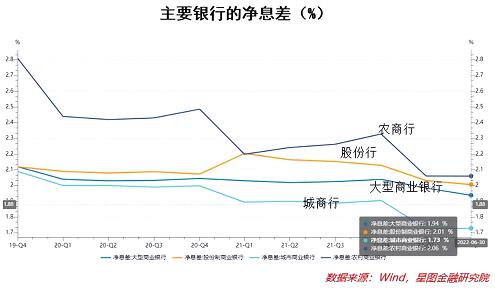
The rate of return on the asset side is falling rapidly, while the debt side is subject to the limit of the benchmark deposit interest rate, which decreases slowly or even rises, resulting in a rapid decline in the bank’s net interest margin, and the net interest margin income is the main source of income for most banks. Therefore, it is bound to affect the overall level of banking operations. Finance is the blood of the real economy, and banks are the most important force in the financial industry. For the economy, “all businesses can be good if a bank is good”, and it is of great significance to stabilize and protect the operation level of the banking industry. To ensure the healthy development of the banking industry and to better support the development of the real economy, it is necessary to work hard from the debt side of the bank to reduce the cost of the bank’s debt, which also requires the bank to reduce the deposit interest rate to achieve.
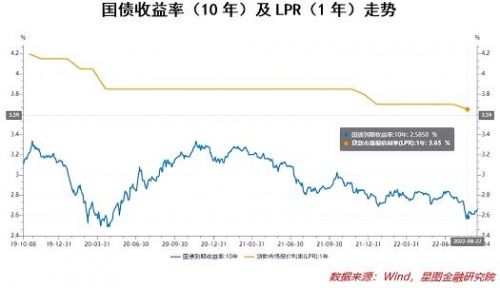
In the face of the marketization of loan interest rates and the rigidity of deposit interest rates, the central bank proposed in the first quarter monetary policy implementation report: the central bank guides the interest rate self-discipline mechanism to establish a market-based adjustment mechanism for deposit interest rates, and the member banks of the self-discipline mechanism refer to the 10-year treasury bond yield. and 1-year LPR to reasonably adjust the deposit interest rate level.
That is to say, the adjustment of bank deposit interest rates in the future will comprehensively refer to the 10-year treasury bond yield and the 1-year LPR interest rate level. Judging from the trend of the two reference interest rates, the decline in deposit interest rates is of course expected.
2
Since the decline in deposit rates is inevitable, the question is, what most people care about is whether deposit rates will continue to fall in the future? This is directly related to the asset allocation of many people. Is it short-term or long-term? Or even put the money in the deposit?
In the short term, it is unlikely that the deposit rate will be lowered again. As mentioned above, deposits are still the most important part of domestic residents’ financial assets. Household savings deposits exceed 80 trillion, involving more than 400 million households and more than one billion depositors. No other product can compare its impact. A short-term readjustment is unlikely. Therefore, whether it is a 3-month, 6-month, 1-year or other short-term deposit, the interest rate is unlikely to change in the short term.
However, from a long-term perspective, the trend of deposit interest rates still depends on the two reference interest rates of the 10-year Treasury bond yield and the 1-year LPR, and there is a high probability that it will continue to decline in the future.
Judging from the process of interest rate marketization in my country, the LPR reform in 2019 basically completed the marketization of loan interest rates, but did not involve the marketization of deposit interest rates. Therefore, from 2019 to the first half of 2022, the anchor of deposit interest rates is still the deposit benchmark. interest rate. This has also led to the continuous reduction of LPR in recent years, but the benchmark deposit rate has not been adjusted, that is, the cost of banks’ liabilities has been declining slowly, and banks’ profit margins have continued to shrink.
After the establishment of the “Deposit Interest Rate Market Adjustment Mechanism” in April this year, the marketization of deposit interest rates has also taken an important step. In the future, the deposit interest rate will also take the 10-year Treasury bond yield and 1-year LPR as the reference benchmark interest rates. When the 1-year LPR is lowered, the deposit rate is likely to be adjusted in parallel soon.
As for the trend of long-term interest rates, from the perspective of the development history of developed countries, the level of interest rates will also decline with the slowdown of economic growth.
3
So, what impact will the overall reduction in deposit interest rates have?
From the perspective of economic development, the decline in interest rates is of course conducive to promoting the economy, especially under the current interference of multiple factors, reducing interest rates and better serving the real economy is of course a good thing for the country and the people. But for many savers, that may not be the case.
First of all, it is the loyal users of bank deposits that are directly affected. However, there is no need to worry about existing users. No matter what type of deposit product it is, the interest rate adjustment is aimed at new deposits after September 15, and has no effect on past deposits.
For such savers with low risk appetite, other alternative products can be selected. Such as monetary funds, pure debt funds, bank cash management financial management tools (such as various baby products of banks), interbank deposit certificate index funds, and products such as increased life expectancy that can lock in long-term yields.
Compared with bank deposits, although these products are not guaranteed by the deposit insurance system like bank deposits, they are very similar to bank deposits in terms of risk, liquidity and profitability, and can replace deposits to a certain extent.
In addition to choosing products with the same capital preservation nature and similar products, it is also an option to appropriately increase personal risk appetite and increase the allocation ratio of equity assets. From the perspective of the development of wealth management, the cost performance of the current equity asset allocation should be significantly improved, such as the reform of the registration system, the improvement of the delisting system, the increase in the proportion of institutional investors, the entry of assets such as Reits, pension and insurance funds. Factors such as the increase in the proportion of market entry have made the development of the equity market increasingly better. In the future, with the transition from indirect financing to direct financing, it will inevitably require a strong capital market. Therefore, for investors with high demand for property appreciation, it is more necessary to increase the allocation ratio of equity assets. However, given the high volatility and high risk of equity assets, this scheme is only suitable for people with higher risk appetite.
The second is the impact on the economy and asset allocation. In theory, the decline in deposit yields will drive residents to “move their deposits” to bank wealth management or other investment products to a certain extent, or promote residents’ consumption. However, from the actual effect, there are more factors affecting residents’ financial management and consumption, such as the performance of the capital market, the expected income of residents in the future, the external economic situation, etc., so it is not absolute.
Finally, the impact on the capital market is good for bank stocks. The drop in deposit interest rate will effectively improve the bank’s net interest margin level, enhance the bank’s profitability, and improve the fundamentals of listed banks. Another more important impact is that the adjustment of the deposit rate this time is an important process of the marketization of the interest rate market. In the future, as the LPR changes, the deposit rate may change synchronously, which will have a far-reaching impact on banks, suppressing the long-term pressure on bank stocks. Valuation factors may change, and bank stocks may usher in a “Davis double-click” market with double-repair valuation performance.
Statement: The copyright of Caijing.com’s column articles belongs to the author himself or relevant rights holders. The articles are only the author’s opinion and do not represent the position of Caijing.com.
