Status: 05/16/2023 10:56 a.m
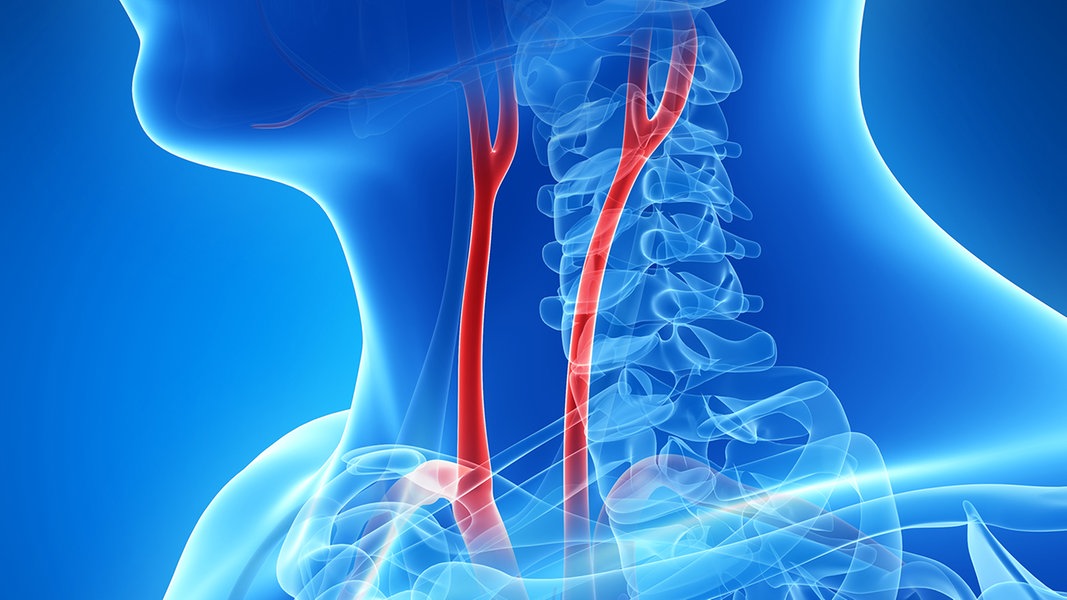
Carotid stenosis, i.e. a narrowing of one of the carotid arteries as a result of arteriosclerosis, is often only discovered by chance. It can lead to a stroke. You should pay attention to these warning signs.
From the age of 65 increases The risk of a stroke is clear, because up to 15 percent of people in this age group have severely narrowed carotid arteries. In more than one million people affected in Germany, calcium deposits (plaques) in a carotid artery (arteria carotis) have already narrowed the blood vessel by more than 50 percent. The carotid arteries running to the left and right of the neck, each with two branches (arteria carotis interna and externa), supply large parts of the brain with blood – and thus with oxygen and nutrients. Carotid stenosis increases the risk of a stroke with possible consequences such as speech disorders, paralysis and lifelong disabilities.
Symptoms: dizziness, deafness, blurred vision
Arteriosclerotic changes, i.e. calcium and fat deposits on the inner walls of the blood vessels, lead to narrowing of the vessels. In the course of this, local inflammatory reactions occur in these areas. The vessel walls can then tear, allowing blood clots to form. These then partially or even completely block the bloodstream. If they detach, they are swept into the brain. They cause a stroke in 20,000 to 30,000 people a year. Early warning signs of a dangerously narrowed carotid artery can include dizziness, numbness, and blurred vision.
Further information
Limit screening to high-risk groups
With an ultrasound examination, the color-coded duplex ultrasound, both the blood flow and the vessel wall can be assessed and the narrowing of the carotid artery caused by calcium deposits can be detected within a few minutes. According to experts, a general examination (screening) for bottlenecks does not make sense.
Annual ultrasound screening of the carotid artery is recommended from the age of 65 if risk factors are present. These include:
- heart diseases
- Diabetes
- peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
- Nicotin consumption
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol (total and LDL cholesterol)
- genetic strain
- little movement
People who have an abdominal aortic aneurysm and, of course, those who have had a stroke or are showing neurological symptoms should also have their carotid artery checked. These include, above all, the so-called transient ischemic attack (TIA), a temporary circulatory disorder in the brain that leads to symptoms of a stroke. However, these disappear completely within seconds or a few minutes. Even if everything seems to be fine again after such an attack, a TIA is often followed by a severe stroke shortly afterwards.
Increasing dementia (vascular dementia) can also be caused by a circulatory disorder. Anyone who is being treated for heart disease can ask the cardiologist to also examine the carotid artery.
Treatment of carotid stenosis
The treatment strategy for constricted carotid arteries depends in particular on whether temporary neurological deficits have already occurred. But the degree of vasoconstriction and the age of those affected also play a role. To put it simply, healthier and younger patients in particular benefit from an operation. The following applies: the higher the stenosis and the more pronounced the symptoms, the greater the benefits of the operation.
reduce risk factors
For all those affected, the focus is on a consistent reduction of risk factors. This includes in particular the treatment of high blood pressure, dyslipidemia and diabetes with medication. In addition, the change in lifestyle with the normalization of body weight, renunciation of nicotine and sufficient physical activity are in the foreground of every therapy. Smoking, diabetes and high blood pressure double the risk of developing carotid stenosis.
Open surgery under local anesthesia or catheter intervention
Planned carotid stenosis operations should only be carried out by experienced specialists in designated specialist centers. Patients who have been recommended such an operation should ideally visit a certified vascular center where such operations are frequently performed. The quality results are included in the centers’ public reports and can be used for decision-making.
In principle, two different methods have been established:
- open operation (Endarterectomy): Vascular surgeons expose the diseased artery, cut it open, and peel out the calcifications. Once the constriction is removed, the blood can flow unhindered to the brain again. The procedure has been tried and tested for more than 20 years and is now preferably carried out under local anesthesia, but general anesthesia is also possible. The advantage of local anesthesia is that the surgeon can identify a stroke or neurological deficits much more quickly and better during the operation. You can then respond immediately and restore blood flow.
- catheter procedure: If there is an increased surgical risk, a special catheter can be pushed through a blood vessel in the groin into the cervical artery in order to expand the constriction there with a balloon and insert a metal vessel support (stent). It should prevent it from growing again. However, this procedure is usually only used in patients who are younger than 70 years of age and whose vessels are not yet too heavily calcified. For those over 70, there is a high risk that a small piece of calcium will come loose when the balloon catheter is inserted and trigger a stroke.
The decision to have surgery must be carefully weighed, because with both procedures it can happen that parts of the calcification are washed into the brain and trigger a stroke. This danger is according to current Studies for open surgery are about 50 percent fewer than for catheter surgery, which is why this is now considered the gold standard.
experts on the topic
Further information