Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF) launches important document. It is the Type 1 Diabetes Index (DT1 Index) which was published in Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology. The DT1 Index is a unique data simulation tool that measures the impact on human and public health of disease in every country in the world.
Up to now, in fact, data on the incidence and impact of DT1 were very incomplete. By leveraging data and insights from the DT1 Index, you can help change the lives of people with this type of diabetes, identifying feasible interventions country by country, including timely diagnosis, accessibility to treatment and funding for research that could lead to a cure that currently does not exist.
Four fundamental moves
Type 1 diabetes carries a great human, emotional and financial burden for those affected and yours prevalence is increasing. Simulations of the DT1 index led to the identification of 4 key interventions that could change the current trajectory of DT1 and its impact on people around the world. Here, in summary, are the objectives to be achieved:
1. Timely diagnosis: Physician education and training needs to be improved for an accurate diagnosis of DT1. If the world population had access to timely diagnosis starting in 2023, 668,000 more people could be alive in 2040;
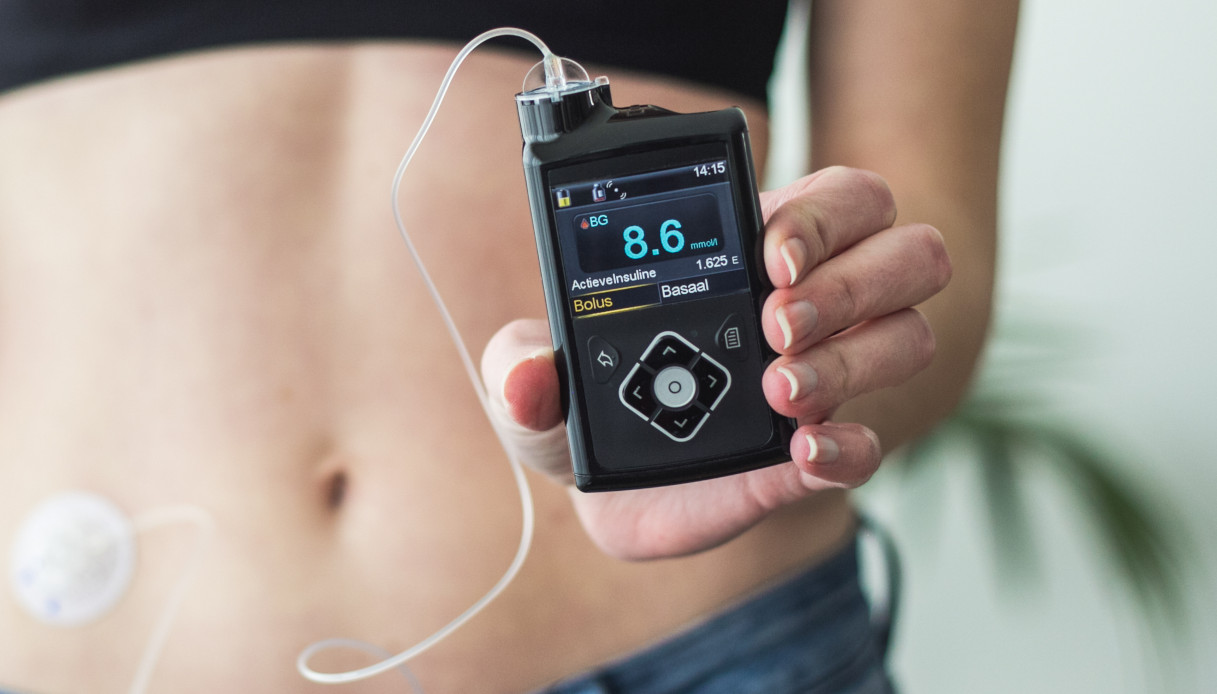
2. Insulin and test strips: It appears important to create barrier-free access to insulin and blood glucose test strips. If the world‘s population had access to insulin and test strips starting in 2023 and trained themselves to manage their condition independently, 1.98 million more people could be alive by 2040;
3. Microinfusori e CGM: the document highlights the importance of guaranteeing access to the technology that automates the glucose monitoring and the administration of insulin. If all DT1 sufferers had access to the technology available from 2023, approximately 673,000 more people could be alive by 2040;
4. Prevention and treatment: leverage further investment and research in emerging prevention, treatments and cures. If treatments were found, 890,000 more people could be alive in 2040.
Once interventions are identified at the global and national levels, the DT1 Index encourages users to take action by sharing data and results with their networks and local decision makers, as well as to connect with other DT1 advocates in their communities.
What type 1 diabetes is and why it needs to be addressed
L’DT1 Index highlights important statistics on the burden of DT1 globally. For example, it is essential to note that this is an increasing disease, given that since 2000, the prevalence of DT1 has increased at a rate 4 times higher than the growth of the world population. To understand how it develops, it is necessary to know the normal functioning of the pancreas.
In the healthy person, insulin works to convert glucose (produced in the liver and created by the digestion of sugars and carbohydrates) into energy. In diabetic people, however, the body does not produce or use insulin properly and this leads to a excess glucose in the blood and then in the urine.
Thus was born the increase in blood sugar, the “key” sign of the disease. Type 1 diabetes, in particular, is characterized by the rapid and progressive decline in insulin production by the pancreas and leads to the complete absence of insulin synthesized by the organ.
It is linked to the production of antibodies that attack and destroy the β cells of the pancreas responsible for producing the hormone. Treatment consists of a controlled diet, exercise and insulin injections as directed by the doctor. In type 2 diabetes, however, the pancreas still produces insulin, but the body cannot use it efficiently to convert glucose into energy.
It is the most widespread form of diabetes, so much so that it accounts for over 90 percent of cases of the disease. For the treatment, the focus is on diet, weight control and possibly the use of drugs to be taken by mouth, in addition to insulin when needed. There is also gestational diabetes, which appears during pregnancy and can if not recognized in time create problems for the mother and to the future baby. Sometimes it disappears after giving birth. It is determined by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, or to use it properly. By itself it does not affect the successful outcome of pregnancy, but it does put you at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the years to come.