Title: Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis: Understanding the Similarities and Differences
Introduction:
Skin conditions can often be confusing and wrongly diagnosed, especially when two conditions closely resemble each other. Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis are two such skin manifestations that share similarities but also exhibit significant differences. It is essential to differentiate between them properly, as both are non-contagious. Let’s delve into the details.
Seborrheic Dermatitis:
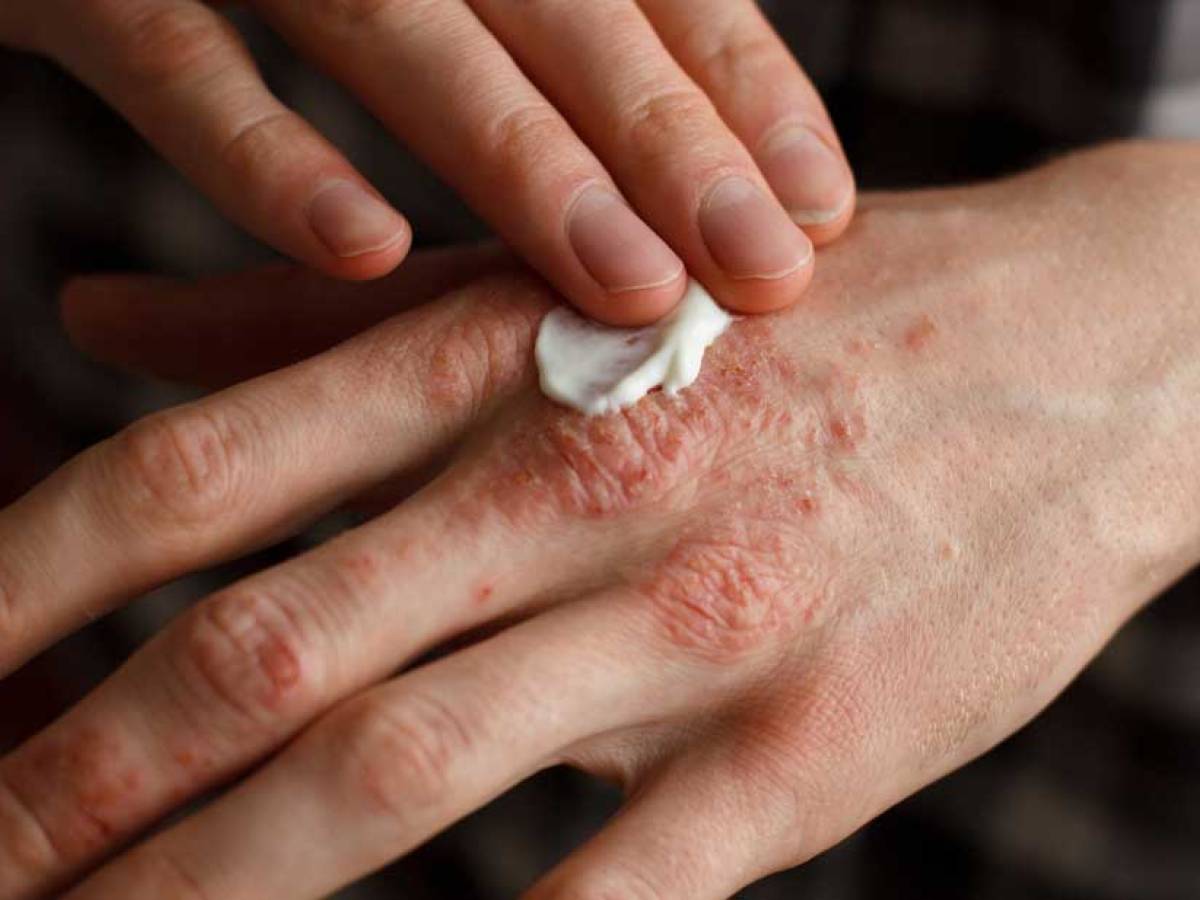
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory and scaly condition primarily affecting the scalp and face. On the face, it commonly appears on the fatty areas, such as the sides of the nose, folds of the sides of the nose, and the area between the eyebrows and eyebrows. The scalp is particularly susceptible to this condition, resulting in inflammatory dandruff that often extends beyond the hairline. Other areas, such as the pubis, beard in men, and breastbone, can also be affected.
The scalp in seborrheic dermatitis exhibits yellowish and oily scales, which may or may not tightly adhere to the scalp. The condition develops in cycles, alternating between active and relatively inactive phases. Factors such as seasons, stress, and specific climatic conditions can trigger or worsen the inflammation. Common symptoms include itching and a burning sensation. This condition is prevalent among adults, affecting approximately 3% of the population. It is also temporary and frequently observed in newborns, known as “cradle cap.”
The Cause and Medical Care:
Seborrheic dermatitis is often triggered by factors such as an excess of sebum, the presence of yeast (Malassezia) on the skin, and the immune response of the individual to these yeasts, leading to skin irritation and inflammation. Treatment typically involves the use of antifungal medications, such as shampoos and face creams. It is crucial to avoid cortisone-containing products on the face, as they can provide short-term relief but worsen skin sensitivity in the long run.
Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is a chronic and non-contagious skin disease that affects about 2-3% of the population. It can manifest at any age, and certain triggering factors can reveal a genetically predisposed terrain. Psoriasis appears as red plaques covered with thick whitish scales, which are narrower than healthy skin. While it commonly affects the elbows and knees (areas prone to microtrauma), it can occur on any part of the skin. The scalp is a preferred area, especially the occipital zone. Inverse psoriasis, less scaly, affects skin folds such as the groin and armpits. The condition can also impact the nails, causing thickening and deformities.
Itching and burning sensations may accompany psoriasis, particularly in skin folds. The impact of psoriasis on an individual’s quality of life can be significant, especially when the condition is widespread or affects visible areas. Psoriatic arthritis, a rheumatological condition, can affect joints and the spine in approximately 25% of individuals with skin involvement. Scalp psoriasis affects both men and women and usually begins before the age of 20 or between 20 and 40 years.
The Cause and Medical Care:
Psoriasis often involves genetic predisposition, and multiple genes play a role in its transmission. Accelerated renewal of the epidermis contributes to the appearance of psoriatic plaques. Various triggering factors include climatic variations, infections, psychological stress, local traumas, certain medications, and associated pathologies or toxic habits. Medical care involves evaluating the extent of psoriasis, its impact, and identifying any underlying conditions. Local treatments, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D derivatives, are typically employed. Regular hydration of the skin and avoiding sudden temperature changes and cold are also recommended.
Conclusion:
Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis may share similarities in terms of skin manifestations, but their causes, treatments, and impacts on individuals’ lives differ significantly. Understanding the distinctions between these conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate medical care. Seeking professional guidance from a healthcare provider can help manage these chronic conditions effectively and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.