What you should know about image quality, high-resolution and blurry images
Anyone who creates content for the web will sooner or later deal with the pixels of images and their resolution in order to optimize the image quality of photos or GIFs. We have put together what terms such as high resolution (high resolution), ppi and pixel density are all about and what makes an optimal image for the web.
What do pixels have to do with images?
Digital images are composed of pixels, small square building blocks or color quadrants. You don’t normally see the individual pixels because they all play together and quickly change color to form the image that we see. However, when you zoom in close or enlarge an image, the small square pixels become visible. If pixels are already recognizable in normal view, then a digital image is of poor quality and looks fuzzy. In this case one also says that the picture is pixelated.
Resolution: what does high resolution mean?
How many pixels an image has determines its resolution. Hi-Res or High Resolution means an image has a high resolution. lo-res or Low Resolution means an image has a low resolution.
Lo-Res images usually have 72 Pixel or color squares per inch (ppi). These images look good on the web because most computer screens can only display this low resolution. Fewer pixels also mean smaller files and therefore shorter loading times for a website.
Hi-Res images have at least 300 Pixel per inch (ppi). This resolution guarantees good print quality and is required if you need to print company brochures or other important materials.
How do you find out the resolution of an image?
Just because an image looks good on the computer doesn’t mean it’s high resolution. The actual height and width of an image also say nothing about it. The file size is also not a clear indication of a high resolution.
To find out the resolution, you need to open the image in an image editing program and Characteristics or call up the image size. You will then see the file size, the height and width of the image (in cm or inches) and the resolution in pixels per inch (ppi). Most computers come preinstalled with a standard image editing program that you can use to find out the resolution.
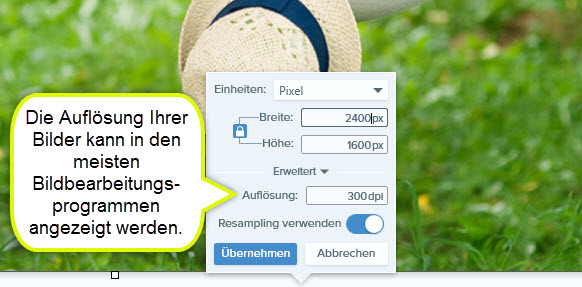
resolution on the screen
Not only digital images, but also digital advertisements are made up of pixels – of course, one ultimately depicts the other. At computer screens and mobile phone displays Resolution is a metric used to evaluate the quality of the display. The resolution of screens corresponds to the total number of pixels in width and height.
You may be familiar with the term 1080p for a computer or television screen. 1080p is a simplified way of saying 1920 × 1080 and means 1920 pixels wide and 1080 pixels high. This is currently the minimum resolution of new PC monitors up to 27 inches. Larger screens can also have higher resolutions. For gaming or professional video editing, a high resolution of at least 2560 x 1440p is recommended.
Also Video cameras have a certain resolution. The most common resolutions today are 1920 x 1080 (1080p or HD) or 3840 x 2160 (2160p or UHD or 4K).
By the way: If you make screencasts or screen recordings, the resolution of your recording is also determined by the resolution of your screen.
Prepare screen recordings and images professionally with Snagit
Record your screen and add annotations, callouts or graphic elements to your images. Create easy how-to guides, GIFs, and videos with Snagit.
Download Free Trial
Resolution versus pixel density
Another important indicator for the quality of screens is the pixel density. It describes the relationship between resolution (i.e. the number of pixels on the screen) and the actual Dimensions Of the screen. The quality and sharpness of a digital image depend not only on the resolution, but also on the pixel density. The higher the pixel density, the sharper the image.
For example, a 24-inch computer screen with a 1080p resolution will provide better picture quality than a 60-inch television screen with the same resolution. For the untrained eye, however, this difference is often hardly noticeable. In recent years, mobile phone manufacturers have engaged in a kind of pixel battle and have rapidly increased the resolution of the relatively small mobile phone displays. This led to a large pixel density on the devices.
New so-called 4K screens have a pixel density four times higher than 1080p and therefore a much sharper picture. The resolution is then, for example, 4096 x 2160. It takes a lot of computer power to support high-resolution displays. This is also the reason why it always takes a while for a new standard resolution to establish itself on the market.
color depth and image quality
Higher resolution makes your image sharper, higher color depth makes it more vivid. Most computer screens have pixels that only Red, Green and Blue (RGB) can produce. Every other color is created by an exact mixture of the three basic colors. Color depth describes the number of colors that a pixel can produce. A higher color depth means more colors and therefore a more realistic and clearer image representation.
Color depth is expressed in bits. Each additional bit means an exponentially higher number of visible colors. The lowest possible color depth is 1 bit to display two colors: black and white, for example. If a pixel has 8 bits, so can 28=256 color tones are displayed. With a standard monitor, the color depth is 24 bits, i.e. 8 bits each for the three primary colors red, green and blue. So can 224 shades can be distinguished. That’s about 16.7 million shades.
How are images sharp for the web?
When adapting an image for the web, it’s worth considering the image’s pixel count and resolution. You don’t necessarily have to upload a high-resolution image; this can even have disadvantages, since computer screens usually cannot display 300 ppi images and the associated large file size affects the loading time. In order to achieve both good display quality and an ideal loading time, images should be optimized for the web before they are uploaded. You should note that:
- First, save your image again before editing to save the keep the original file. That way nothing is lost. Image information cannot be added later.
- Get your image in the right format: Through crop or trimming, you can reduce the file size without sacrificing image quality. If your image is very large (in width and length) and too large for the destination, you can also reduce it before uploading. However, be careful to maintain the aspect ratio and not stretch or compress the image.
- If you use the image for the web, one is enough Resolution of 72 ppisince most screens cannot display a higher resolution.
- Also pay attention to the color settings: if you create an image for digital signs and displays, it should be suitable for the RGB color space saved, since computer displays can only show the 3 primary colors red, green and blue.
- Save your image as PNG to avoid loss of quality and to be able to edit the image further. JPGs are also suitable as a web format, but are associated with compression, which can lead to loss of quality. What else you should know about image formats.
Some image editing programs also offer the option “Optimize image for web” – here you can use web-optimized presets for your image. Since images for the web usually have a low resolution, i.e. are Lo-Res, they are usually not suitable for printing. This means that when you download an image from a website, the print quality is usually not good enough.
