The global market ushered in a carnival night.
Just now, the world‘s attention U.S. inflation data was released, and in October, both were significantly lower than market expectations. Affected by this, the three major U.S. stock indexes opened higher across the board, and then continued to strengthen. As of 23:30 Beijing time, they had risen by more than 830 points, an increase of more than 2.5%, a surge of more than 5.4%, and a rise of more than 4%; European stock markets also collectively pulled sharply. It rose by more than 3%; in addition, it also rose in a straight line, once rising by more than 2%.
The main reason why the market reacted so strongly to the October CPI data in the United States is that the inflation rate in the United States, which continues to be “out of the table”, seems to be showing signs of cooling. According to this, the market expects that the Fed’s interest rate hike storm may stop. After the data was released, the market consensus was that the probability of the Fed raising interest rates by 50 basis points in December far exceeded 75 basis points.
However, it is worth noting that under the storm of interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, the risk of a recession in the United States has once again sounded the alarm. UBS warned in its latest report that the U.S. may not be able to avoid a hard landing next year, with a “severe” contraction starting at the end of the first quarter or early in the second quarter of next year. The UBS report model shows that the probability of the U.S. economy entering a recession in September next year exceeds 60%.
A piece of data detonates the global market
The just disclosed US CPI data completely detonated the global market.
On the evening of November 10, Beijing time, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics officially disclosed the consumer price index (CPI) for October. The U.S. CPI in October rose by 7.7% year-on-year, which was lower than the market expectation of 7.9% and fell sharply from the previous value of 8.2%. ; October CPI rose 0.3% month-on-month, also better than market expectations of 0.5%, and the growth rate fell sharply from the previous value of 0.6%.
In addition, the US core inflation rate, which the market and the Fed are more concerned about, was also better than expected. The data shows that after excluding the volatile food and energy prices, the core CPI rose by 6.3% year-on-year, lower than the market expectation of 6.5% and lower than the previous value of 6.6%; the core inflation rose by 0.3% month-on-month, lower than the market expectation of 0.5%. %, a sharp drop from the previous value of 0.6%.
Image from the author
Stimulated by better-than-expected inflation data, the three major U.S. stock indexes opened higher across the board, and then continued to strengthen. As of 23:30 Beijing time, the Dow Jones index rose more than 830 points, or more than 2.5%, the Nasdaq soared more than 5.4%, and the S&P 500 The index rose more than 4%.
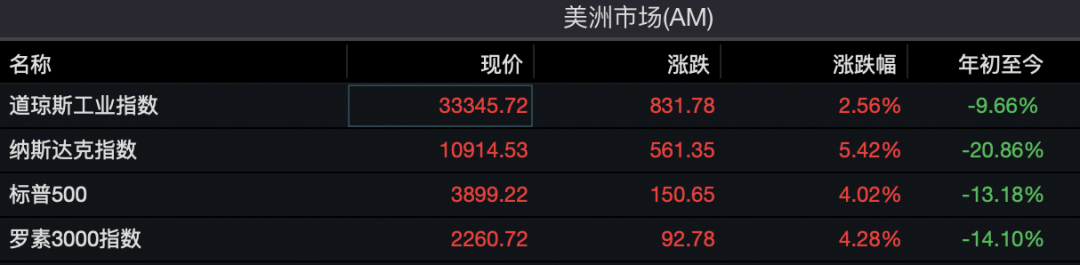
Large technology stocks also rose across the board. As of 23:30 Beijing time, Amazon (NASDAQ: ) surged by more than 9.6%, Google (NASDAQ: ) rose by more than 6.7%, Apple (NASDAQ: ) rose by more than 6%, Tesla (NASDAQ: ) rose more than 5%. Chinese stocks also strengthened collectively. The Nasdaq China Golden Dragon Index soared by 7.8%, Bilibili soared by more than 17%, Weilai Motors rose by more than 13%, Xiaopeng Motors rose by 8%, and Alibaba rose by more than 7% .
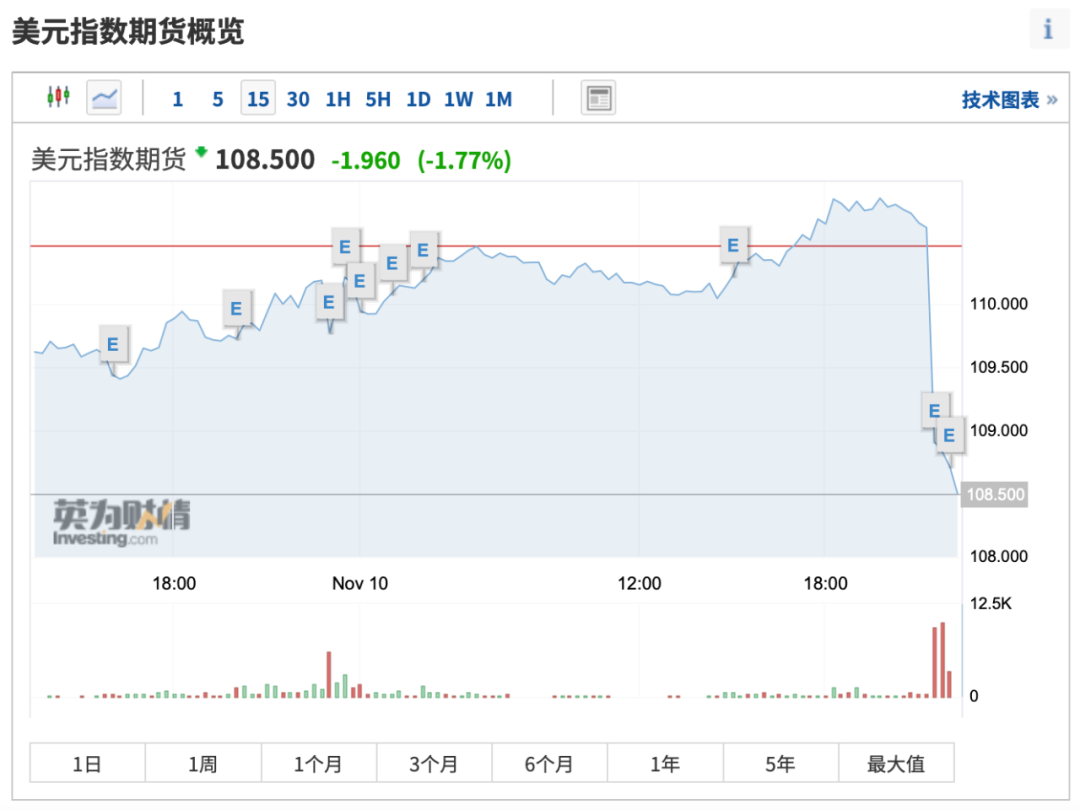
As of 22:30 Beijing time, the short-term decline was more than 190 points, and it is now at 108.50, down 1.77% in the day. The U.S. bond market also ushered in a carnival, in which the decline in yields expanded to 25 basis points;
At the same time, European stock markets have also risen in a straight line. As of 23:30 Beijing time on Thursday, the European Stoxx 50 index rose by more than 3%, up 3.5%, up 2.6%, up 2.2%, and up 1.2%.
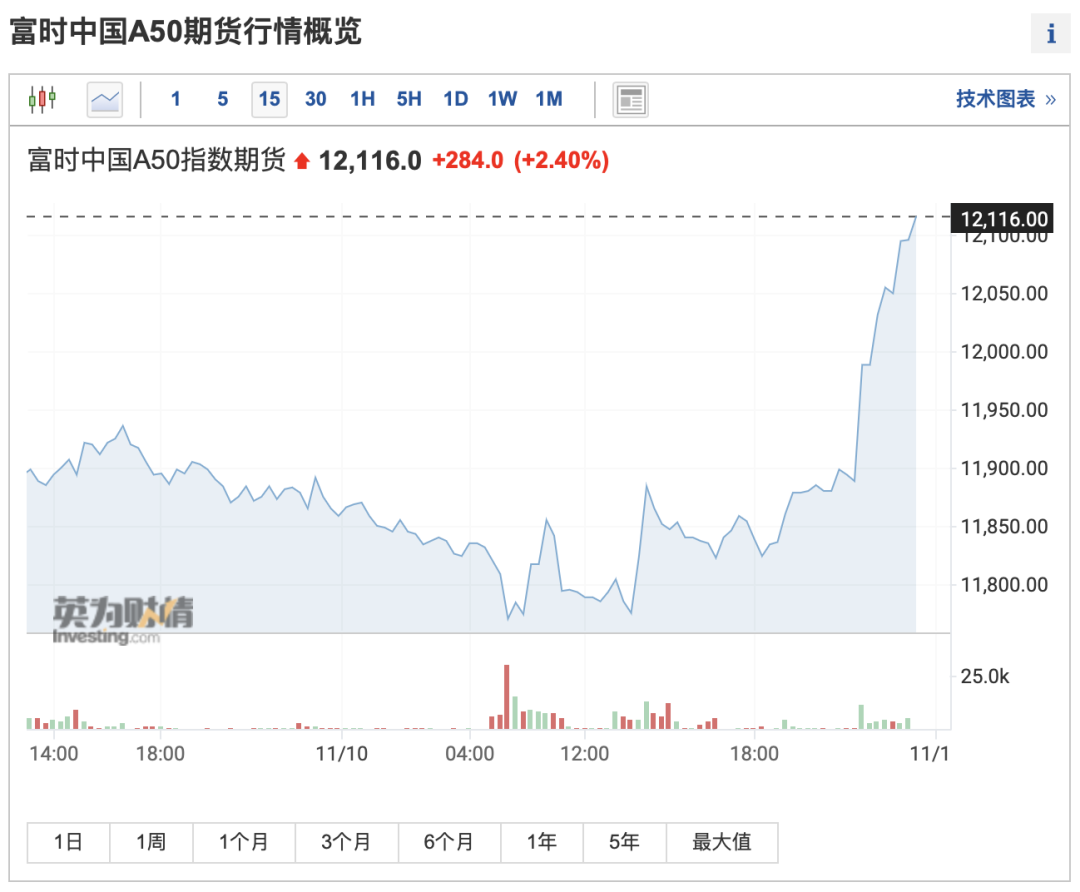
In addition, the FTSE China A50 Index futures also rose in a straight line, rising by more than 2.4% at one time; it continued to rise, and once rose more than 900 points within a day, an increase of more than 1%.
Looking specifically at the US CPI data for October, significant declines in energy services, gasoline prices and used car costs led to a lower-than-expected CPI data.
In terms of core inflation, the All Items Index excluding food and energy rose 0.3% in October, following a month-on-month rise of 0.6% in September, with rising rental costs being the dominant factor. It rose 0.8% in October, the largest monthly gain since August 1990.
It is worth mentioning that on the eve of the release of the US CPI data, Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida and Bank of Japan Governor Kuroda Haruhiko held an emergency meeting, showing vigilance against this CPI data, because the previous inflation data caused the yen to fall sharply. .
After the meeting, Haruhiko Kuroda told the media that the recent rapid unilateral depreciation of the yen is not good for the Japanese economy, and the Bank of Japan will pay due attention to the financial and foreign exchange markets. The just-announced inflation data may also let the Japanese authorities breathe a sigh of relief.
The rate hike storm has stopped?
After the latest U.S. inflation data is released, the focus of the global market will turn to the Federal Reserve. Will the rate hike storm continue?
According to the schedule, the next interest rate meeting of the Federal Reserve will be held on December 14, local time, and the October inflation report will undoubtedly be one of the important references for the next interest rate meeting. The analysis pointed out that inflation fell faster than expected in October, and the Fed will have more room to slow down the pace of interest rate hikes.
Before the October inflation data was revealed, the OIS market had fully priced in expectations of a 50 basis point rate hike by the Fed in December, and projected a 45% chance of a 75 basis point rate hike by the Fed in December.
After the data was disclosed, the market generally expected that the probability of raising interest rates by 50 basis points in December far exceeded 75 basis points. According to CME Group’s FedWatch tool, the probability of the Fed raising rates by 50 basis points is 80%, and the probability of the Fed raising rates by 75 basis points falls below 20%.
Currently, traders in U.S. short-term interest rate futures expect the federal funds rate to peak at 4.75%-5% by March 2023. Financial website Forexlive said the inflation report lays the groundwork for the rest of the year, or at least until the Dec. 13 CPI figures.
The Wall Street Journal reporter Nick Timiraos, “The Fed’s microphone”, said that the October inflation report could lead the Fed to raise interest rates by 50 basis points next month as planned. After the data was released, Philadelphia Fed President Harker also made a speech, saying that raising interest rates by 50 basis points is still significant, and his support for suspending interest rate hikes when interest rates reach around 4.5%.
Last week, Powell said at a news conference that long-term inflation expectations remain solid, that price pressures on goods and services remain evident, and that he will remain firmly committed to achieving his 2 percent inflation target. But he also hinted that the Fed will slow the pace of rate hikes in December.
At the same time, Chicago Fed President Evans also issued a clear dovish signal. He said on Wednesday that even if inflation continues to outpace expectations in the coming months, now is the time to start slowing rate hikes given that the Fed has raised interest rates so high.
US recession warning
Since 2022, the Federal Reserve has launched a rare storm of interest rate hikes in history. The cumulative rate hike during the year has reached 375 basis points, which not only brought a severe impact to the US stock market, but also dragged the US economy to the brink of recession.
At present, “recession” has become the most frequent keyword for Wall Street’s outlook on the U.S. economy in 2023, with warnings from big banks such as Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, JPMorgan Chase, Nomura Securities, and UBS Group one after another.
UBS has been particularly vocal in its downvote on the U.S. economy. UBS warned again in its latest report that the U.S. may not be able to avoid a hard landing next year.
UBS said the current U.S. growth momentum will taper off in the coming months, and pressure from higher interest rates will see the economy begin to contract “severely” in the late first or early second quarter of next year. The UBS report model shows that the probability of the U.S. economy entering a recession in September next year exceeds 60%. Specifically, UBS expects U.S. real GDP to contract by about 1% next year for eight months, a slightly milder recession than in 1991.
Meanwhile, UBS expects U.S. employment to continue to decline in the coming year amid the recession looming. Its models suggest unemployment will rise by around 2 percentage points to a peak of 5.5% by 2024.
Based on U.S. recession expectations, UBS predicts that U.S. stocks will suffer a new round of selling by mid-2023, with the S&P 500 expected to fall to 3,200 in the second quarter of next year.
Hani Redha, portfolio manager at PineBridge, also expects U.S. stocks to fall further in the coming months as the Fed’s tightening of monetary policy will push the U.S. economy into recession in 2023.
But U.S. President Joe Biden seems very optimistic. Biden said at the White House midterm election press conference on November 9 that in terms of economic growth, the United States is not yet close to a recession. Biden believes the U.S. can achieve what most economists call a soft landing, while being able to gradually lower prices without ultimately having to fall into a recession.
But Biden does not seem optimistic about the inflation that the market is worried about. Biden said there is no guarantee the U.S. will be able to escape inflation, and actions to lower it will take more time to take effect.
At the same time, the European economy is also sounding the alarm of recession. On November 10, local time, the European Central Bank predicted that the economy will weaken further by 2023.
Andrew Cunningham, chief European economist at Capital Economics, a British economic research institution, said bluntly that the euro zone is already on the brink of recession.
